Gasoline Market Overview:
The global gasoline market is steadily expanding, driven by rising demand in areas such as transportation, industrial uses, and energy production. This market encompasses a wide range of gasoline products, from conventional fuel to high-performance variations, catering to both consumer and business demands. Our paper provides a detailed examination of procurement trends, with an emphasis on cost-cutting methods and the use of sophisticated technology to improve supply chain and distribution operations.
Looking ahead, the gasoline business has several significant procurement problems, including controlling volatile fuel costs, ensuring resilience in the supply chain, maintaining environmental compliance, and incorporating sustainable practices into production and distribution. Digital technologies and strategic sourcing activities are critical in improving procurement procedures and ensuring long-term market competitiveness. The global demand continues to grow, companies are increasingly leveraging market intelligence to drive operational efficiency, minimize risks, and stay ahead of industry shifts.
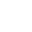
- Market Size: The global Gasoline market is projected to reach USD 2900 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of approximately 2.45% from 2025 to 2035.
Growth Rate: 2.45%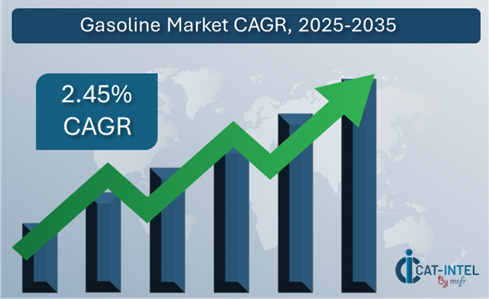
- Sector Contributions: Growth in the market is driven by:
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain Optimization: There is a growing demand for real-time data and process integration to improve fuel production and distribution operations.
- Retail and Distribution Growth: Retail fuel shops and e-commerce platforms are becoming more reliant on modern technology for inventory management, demand forecasting, and customer relationship management (CRM).
- Technological Transformation: Advances in data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are improving gasoline distribution, optimizing logistics, and providing predictive insights into fuel demand and pricing.
- Innovations: The emergence of modular fuel supply solutions, which enable enterprises to adapt and integrate systems to suit unique demand while lowering operational costs and complexity.
- Investment Initiatives: Significant investments in electronic platforms and technologies, including cloud-based systems, will help to minimize infrastructure costs and increase fuel distribution and management flexibility.
- Regional insights: North America and Asia Pacific continue to be important contributors, thanks to robust digital infrastructure and a growing move toward tech-driven fuel supply solutions.
Key Trends and Sustainability Outlook:
- Cloud Integration: Cloud technologies are widely used to create scalable, cost-effective fuel management systems that provide improved tracking, analytics, and remote access.
- Advanced Features: Integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain technologies to improve decision-making, automate processes, and boost transparency in fuel source and distribution.
- Sustainability Focus: Gasoline supply chains are increasingly prioritizing resource optimization, environmental impact elimination, and sustainability goals, which are backed by cutting-edge tracking and reporting technologies.
- Customization Trends: There is an increasing demand for customized solutions in industries such as transportation, automotive, and energy to fulfil specific fuel source and distribution requirements.
- Data-Driven Insights: Advanced analytics help fuel companies forecast demand and optimize distribution routes and track performance metrics for better market responsiveness.
Growth Drivers:
- Digital Transformation: Using modern digital technology in petroleum production, distribution, and retail operations to boost productivity, efficiency, and consumer happiness.
- Demand for Process Automation: A growing dependence on automation in gasoline supply chains to optimize operations and decrease operational bottlenecks, resulting in faster delivery and lower prices.
- Scalability Needs: Fuel firms are looking for scalable solutions that can handle worldwide expansion, dynamic pricing models, and local regulatory needs.
- Regulatory Compliance: The gasoline business is under increased scrutiny for environmental rules and reporting standards, and digital technologies can help ensure adherence to compliance guidelines.
- Globalization: In the increasingly global gasoline market, there is a growing demand for systems that allow for multi-currency, multi-lingual, and international regulatory compliance.
Overview of Market Intelligence Services for the Gasoline Market:
Recent investigations have highlighted major issues in the gasoline business, including increased production and operational expenses, as well as a growing need for supply chain efficiency. Market intelligence studies give practical insights that assist firms identify opportunities to reduce expenses, optimize supplier relationships, and enhance overall operational efficiency. These insights are also critical in assuring compliance with legislative and industry requirements, maintaining high quality standards, and successfully controlling expenses.
Procurement Intelligence for Gasoline: Category Management and Strategic Sourcing
To remain competitive in the gasoline market, businesses are improving procurement processes via efficient supply chain management and vendor performance evaluation. Strategic sourcing and category oversight are critical for lowering procurement costs, guaranteeing a consistent supply of high-quality fuel, and managing market swings. Businesses can leverage actionable market intelligence refine their procurement strategies, negotiate favourable terms with fuel suppliers, and ensure the long-term stability and competitiveness of their operations.
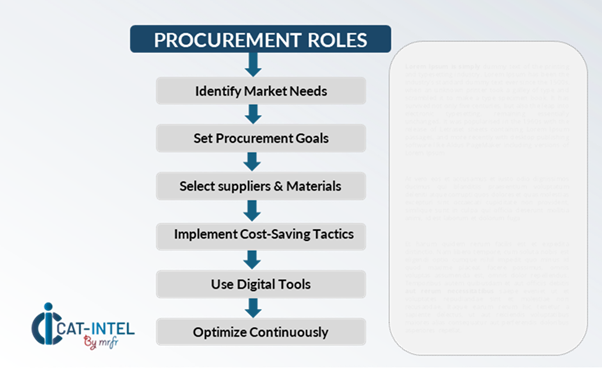
Pricing Outlook for Gasoline: Spend Analysis
The gasoline pricing outlook is projected to remain moderately dynamic, with potential fluctuations caused by a variety of variables. Crude oil price variations, developments in refining technology, shifts in demand for alternative fuels, and regional price variances are all important factors to consider. Furthermore, the increased use of digital tools for fuel supply chain optimization, combined with rising concerns about sustainability, environmental rules, and energy security, is putting upward pressure on gasoline prices.
Graph shows general upward trend pricing for Gasoline and growing demand. However, there may be fluctuations influenced by economic conditions, technological advancements, and competitive dynamic.
To cut expenses, organizations could optimize procurement procedures, improve supplier management, and investigate flexible fuel sourcing alternatives. Using digital solutions for real-time market monitoring, price forecasting with advanced analytics, and effective contract administration can dramatically reduce costs.
Partnering with dependable fuel suppliers, negotiating long-term agreements, and exploring subscription-based pricing or hedging options are all critical measures for effectively managing gasoline procurement costs. Regardless of future pricing problems, prioritizing supply chain resilience, increasing efficiency, and investing in sustainable practices will be crucial for long-term cost-effectiveness and operational excellence.
Cost Breakdown for Gasoline: Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Cost-Saving Opportunities
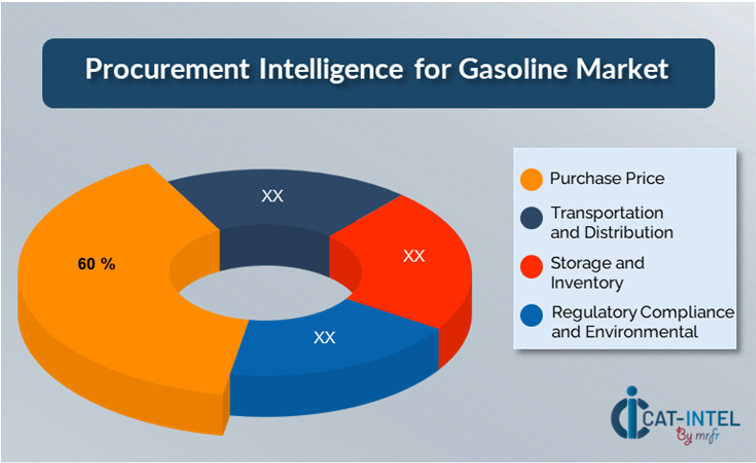
- Purchase Price: (60%)
- Description: The purchase price of gasoline is the amount paid per unit of gasoline, which is determined by factors such as crude oil prices, refinery costs, market demand, geopolitical events, and the worldwide supply-demand balance.
- Trend: The purchase price of gasoline is becoming more unpredictable, driven by fluctuating global oil prices, geopolitical tensions, and a transition toward renewable energy sources, with a greater emphasis on price forecasting and hedging techniques to reduce cost risks.
- Transportation and Distribution: (XX%)
- Storage and Inventory: (XX%)
- Regulatory Compliance and Environmental: (XX%)
Cost-Saving Opportunities: Negotiation Levers and Purchasing Negotiation Strategies
In the gasoline sector, streamlining procurement processes and using strategic bargaining strategies can result in significant cost savings and increased operational efficiency. Long-term relationships with dependable gasoline suppliers, particularly those that provide flexible and scalable delivery models, can result in more attractive price structures and terms, such as volume-based discounts and bundled service packages. Multi-year contracts and subscription-based pricing structures offer chances to secure reduced rates and protect enterprises from price volatility over time.
Collaborating with suppliers who prioritize innovation and sustainability provides additional benefits, such as access to advanced data analytics, IoT integration, and environmentally friendly fuel alternatives, which can help reduce long-term operational costs and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Implementing digital procurement technologies like supply chain management platforms and fuel consumption analytics improves transparency, reduces overordering, and ensures more efficient gasoline utilization.
Supply and Demand Overview for Gasoline: Demand-Supply Dynamics and Buyer Intelligence for Effective Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
The gasoline market is steadily expanding, driven by rising demand in areas such as transportation, energy generation, and retail. Factors influencing supply and demand dynamics include technological breakthroughs in fuel production, regulatory standards, and global economic situations.
Demand Factors:
- Digital Transformation and Efficiency Enhancements: The growing requirement for efficient fuel management, real-time tracking, and automated logistics drives demand for innovative fuel management systems.
- Shift Towards Sustainable Fuels: As governments and businesses work to reduce carbon emissions, demand for alternative fuels like biofuels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure is increasing.
- Regulatory Compliance Requirements: Increasing regulatory expectations for emissions reductions and fuel efficiency standards are driving the market for specialized fuel solutions and compliance systems, notably in transportation and industry.
- Integration Capabilities: The demand for seamless integration of gasoline supply chains, retail networks, and sophisticated technology systems (such as IoT-enabled fuel monitoring) is increasing, which improves operational efficiency.
Supply Factors:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in gasoline refining, renewable energy technologies, and supply chain automation are increasing fuel suppliers' competitiveness and driving progress in fuel production and distribution.
- Vendor Ecosystem: A diversified selection of fuel suppliers, from huge international corporations to niche, region-specific providers, guarantees consumers and businesses have a variety of options, which promotes competition and market growth.
- Global Economic Factors: Changes in crude oil prices, geopolitical conflicts, and trade policy affect the availability and cost of gasoline and other fuels.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Supply networks are evolving in response to the increased demand for flexible and scalable fuel solutions that can meet changing regional requirements, from high-demand metropolitan regions to distant rural locales.
Regional Demand-Supply Outlook: Gasoline
The Image shows growing demand for Gasoline in both North America and Asia Pacific, with potential price increases and increased Competition.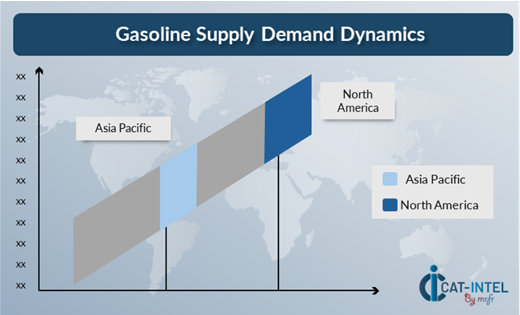
North America: Dominance in the Gasoline Market
North America, particularly the United States, is a dominant force in the global Gasoline market due to several key factors:
- High Demand for Energy: North America, notably the United States, is one of the world's major gasoline consumers due to a vast number of automobiles, a large industrial sector, and significant transportation requirements.
- Strong Infrastructure: The region is home to multiple refineries, pipelines, and storage facilities that assure a consistent and dependable supply of gasoline to suit domestic and worldwide demands.
- Technological Innovation: The region is a pioneer in energy innovation, with advances in fuel production technology, fuel efficiency, and greener alternatives such as biofuels. These technologies contribute to the optimization of gasoline manufacturing processes, cost reductions, and environmental requirements.
- Stable Economic Conditions: North America, especially the U.S. and Canada, have stable economies that support high gasoline consumption. Economic growth is high.
- Energy Independence: The United States has made tremendous progress toward energy independence, primarily through domestic oil production (e.g., shale oil). This lessens North America's dependency on imports while strengthening its position as a leading player in the global gasoline market.
North America Remains a key hub Gasoline Price Drivers Innovation and Growth
Supplier Landscape: Supplier Negotiations and Strategies
The gasoline market's supplier landscape is similarly diversified and competitive, with global oil giants and regional fuel providers influencing important market dynamics. These providers play an important role in deciding on pricing structures, fuel availability, sustainability measures, and supply chain efficiency. Large global oil firms dominate the industry, offering a diverse range of fuel products and services, while smaller, regional competitors focus on local demand, specialty fuel solutions, and innovative sustainable energy options.
The gasoline supplier ecosystem includes major global players such as ExxonMobil, Shell, and BP, as well as local suppliers that cater to specific regional needs or provide specialized fuel products such as biofuels and electric vehicle charging solutions. As companies and governments prioritize energy efficiency, sustainability, and regulatory compliance, gasoline providers are developing technologies in fuel production, refining, and delivery, while also offering flexible pricing structures, long-term contracts, and supply chain solutions to meet evolving market demands. This evolving landscape reflects the increasing importance of digital transformation and operational efficiency within the gasoline industry.
Key Suppliers in the Gasoline market include:
- ExxonMobil
- Royal Dutch Shell.
- BP
- Chevron
- TotalEnergies
- Saudi Aramco
- Valero Energy
- ConocoPhillips
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL)
- Petrobras
Key Developments Procurement Category Significant Development:
|
Significant Development |
Description |
|
Market Growth |
The gasoline industry is expanding rapidly, propelled by rising worldwide energy demand and increased consumption in key sectors such as transportation, industrial, and retail, particularly in emerging nations. |
|
Cloud Adoption |
The demand for real-time monitoring, tracking, and data-driven insights in gasoline distribution is driving enterprises to adopt cloud solutions, particularly in countries that are implementing hybrid work models and smart infrastructure technologies. |
|
Product Innovation |
The combination of AI-powered analytics and real-time data processing improves efficiency in fuel production, distribution, and supply chain management, allowing firms to optimize operations and cut costs. |
|
Technological Advancements |
The use of robots and automation in gasoline production and distribution facilities streamlines operations, improves accuracy, and reduces human error, resulting in increased efficiency in meeting demand. |
|
Global Trade Dynamics |
Global economic policies, trade restrictions, and compliance standards. Multinational oil businesses and fuel distributors must negotiate regulatory changes while modifying their tactics to preserve compliance and a competitive edge across locations. |
|
Customization Trends |
Companies are looking for more adaptable and tailored solutions to meet unique market demands, such as modular systems that can combine with other technologies like renewable energy or electric car infrastructure. |
|
Gasoline Attribute/Metric |
Details |
|
Market Sizing |
The global Gasoline market is projected to reach USD 2900 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of approximately 2.45% from 2025 to 2035. |
|
Gasoline Technology Adoption Rate |
Around 60% of petroleum and energy firms have implemented sophisticated fuel management systems, with a noticeable move toward digital platforms and cloud-based solutions for increased scalability, real-time tracking, and data integration. |
|
Top Gasoline Industry Strategies for 2025 |
Key gasoline market strategies for 2024 include using data-driven technologies to manage fuel supply chains, integrating AI and machine learning for demand forecasting and route optimization, and emphasizing sustainability initiatives by incorporating renewable energy solutions. |
|
Gasoline Process Automation |
Approximately 50% of gasoline supply chain operations use automation, notably for regular tasks like fuel replenishment, predictive maintenance, and compliance reporting. |
|
Gasoline Process Challenges |
Key issues in the gasoline business include unpredictable pricing due to geopolitical factors, expensive infrastructure costs for integrating new technologies, regulatory compliance complexities, and environmental concerns about carbon emissions. |
|
Key Suppliers |
ExxonMobil, Shell, BP, and Chevron are among the world's largest gasoline providers. These companies provide a wide range of fuel products and services, including regular gasoline and environmentally friendly fuel alternatives. |
|
Key Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are among the most important regions for gasoline consumption. These areas have high demand due to transportation needs, industrial activity, and the growing acceptance of sustainable fuel options. |
|
Market Drivers and Trends |
The gasoline industry is expanding due to rising energy consumption, especially in emerging nations, as well as the continuous transition towards sustainable fuel options, including biofuels and electric vehicle infrastructure. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Our procurement intelligence services offer comprehensive market analysis for gasoline sourcing, identifying key suppliers and evaluating industry trends. We provide spend analysis, supplier assessments, and strategic sourcing guidance to help secure reliable fuel supply at competitive prices.
We assist in evaluating the TCO for gasoline by accounting for factors such as fuel purchase prices, logistics costs, storage expenses, and environmental compliance. This holistic analysis ensures a clear understanding of the overall financial impact of fuel sourcing and supply chain management.
Our risk management services address issues such as price volatility, supply disruptions, geopolitical risks, and regulatory changes. These strategies help mitigate risks associated with fuel procurement, ensuring a reliable and cost-effective fuel supply.
Our Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) services focus on strengthening partnerships with fuel suppliers. We assist in negotiating favourable contracts, evaluating supplier performance, and fostering long-term relationships to ensure consistent supply and competitive pricing.
We recommend best practices such as supplier diversification, demand forecasting, risk mitigation strategies, and regular performance monitoring. These practices ensure efficient and cost-effective gasoline procurement, mitigating supply chain vulnerabilities.
Digital tools enhance gasoline procurement by automating supply chain management, improving demand forecasting, and providing real-time tracking of fuel deliveries. These technologies streamline operations, reduce costs, and optimize fuel distribution networks.
Our supplier performance management services track metrics such as fuel quality, delivery timeliness, and customer service responsiveness. This ensures that suppliers maintain reliable performance, helping businesses optimize their fuel procurement strategy.
We support negotiations by leveraging market insights, analysing fuel price trends, and utilizing strategies like multi-year agreements, volume discounts, and flexible delivery terms. These tactics help secure favourable terms and ensure stable pricing over time.
We provide tools that offer detailed insights into global fuel price trends, supplier capabilities, and logistics forecasts. These resources enable data-driven decisions in your gasoline procurement strategy, helping to identify cost-saving opportunities and market dynamics.
We help ensure compliance with environmental regulations, safety standards, and industry-specific requirements. This includes verifying that fuel suppliers meet local and international regulatory standards, such as emissions and safety protocols.
We recommend maintaining multiple supplier relationships, diversifying fuel sources, and leveraging cloud-based fuel management solutions to anticipate and mitigate potential supply chain disruptions. Establishing contingency plans ensures a consistent and reliable fuel supply.
Our tracking solutions monitor metrics like fuel quality, on-time delivery, pricing consistency, and customer service. This helps assess supplier reliability and informs future sourcing decisions, ensuring long-term stability in gasoline procurement.
We focus on identifying suppliers that offer more sustainable fuel alternatives, such as biofuels, and prioritize suppliers with a commitment to reducing carbon emissions. These practices align with your organization’s sustainability objectives and support greener fuel sourcing.
Our pricing analysis compares fuel rates across different suppliers and tracks price fluctuations in the global fuel market. By leveraging these insights and employing negotiation strategies, we help secure cost-effective gasoline procurement while ensuring reliable and high-quality fuel supply.
We help mitigate fuel price volatility by employing strategies such as hedging, establishing long-term contracts with fixed pricing, and diversifying supplier sources. These approaches allow businesses to lock in favourable rates and protect against sudden price increases, ensuring more predictable fuel costs.