
Automotive Over The Air Updates Market Trends
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Research Report Information By Technology (Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA], Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]), By Application (Electronic Control Unit (ECU), Infotainment, Safety & Security, Telematics Control Unit (TCU), others ) By Propulsion (ICE, Electric Vehicle), By Vehicle Type (Passenger Car, Light Commercial Vehicle, Heavy Commercial Vehicle)–M...
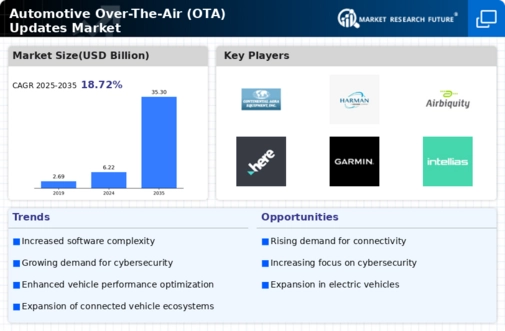
Market Summary
As per Market Research Future Analysis, the Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from USD 5.34 billion in 2023 to USD 14.95 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 18.72% from 2024 to 2030. The growth is driven by increasing connectivity in passenger cars and the demand for advanced software updates. The Software over-the-air (SOTA) segment holds the largest market share, primarily due to the rise in infotainment applications. The Telematics Control Unit (TCU) segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR, fueled by advancements in telecommunication applications. North America leads the market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific, with significant growth anticipated in the latter region due to major automotive hubs.
Key Market Trends & Highlights
Key trends driving the Automotive OTA Updates Market include the rise in demand for connected vehicles and advancements in technology.
- Market size in 2022: USD 4.5 billion; projected to reach USD 14.95 billion by 2030. CAGR from 2024 to 2030: 18.72%; driven by increasing connectivity in vehicles. SOTA segment holds the largest market share due to growing infotainment applications. TCU segment expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
Market Size & Forecast
| 2022 Market Size | USD 4.5 billion |
| 2023 Market Size | USD 5.34 billion |
| 2030 Market Size | USD 14.95 billion |
| CAGR from 2024 to 2030 | 18.72% |
| Largest Regional Market Share in 2022 | North America. |
Major Players
<p>Key players include Robert Bosch GmbH, NXP Semiconductors N.V, Verizon Communications Inc., Continental AG, Infineon Technologies AG, Qualcomm Incorporated, Intel Corporation, HARMAN International, Airbiquity Inc, Aptiv, HERE Technologies, BlackBerry QNX Software Systems Limited, Garmin Ltd., Intellias Ltd.</p>
Market Trends
Rise In Demand For Connected Vehicles is driving market growth
Connected cars facilitate wheel connectivity, offering comfort, convenience, performance, safety, security, and powerful network technology. This enables drivers to connect to online platforms, thereby facilitating real-time communication. The rise in consumer demand for connectivity solutions, the surge in need for constant connectivity, the increase in dependency on technology, and the surge in the tech-savvy population are the key factors contributing to market CAGR growth in demand for global connected cars. Network connectivity solutions such as vehicle-2-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) systems can share content with various devices inside and outside a vehicle.
In a vehicle connected to various devices, the driver receives real-time data around the vehicle to increase safety. The main goals of connected car adoption are to avoid collisions, reduce fatalities, and increase fleet management efficiency.
Additionally, by strengthening collaboration with solution providers and partners, automotive OEMs optimize R&D spending to prioritize connected car programs. For instance, in 2021, Ford and Google announced their unique strategic partnership to accelerate Ford's transformation and reinvent the connected car experience with embedded Google apps and services. Similarly, in 2019, Airbiquity announced that it had become a member of the Japan Automotive Software Platform and Architecture (JASPAR), which promotes the standardization of automotive software and networks to improve development efficiency and stability.
Thus, manufacturers' rise in the adoption of connected car devices is expected to increase the growth of the surveillance automotive over-the-air market revenue during the forecast period.
<p>The ongoing evolution of automotive technology suggests that Over-The-Air updates are becoming increasingly vital for enhancing vehicle performance and ensuring cybersecurity, thereby reshaping the landscape of the automotive industry.</p>
U.S. Department of Transportation
Automotive Over The Air Updates Market Market Drivers
Market Growth Projections
The Global Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Industry is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. With a market value of 6.22 USD Billion in 2024, it is anticipated to expand significantly, reaching an estimated 35.3 USD Billion by 2035. This growth trajectory reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.08% from 2025 to 2035. The increasing adoption of connected vehicle technologies, coupled with the rising demand for software updates and enhancements, is likely to drive this expansion. As manufacturers continue to invest in OTA capabilities, the market is poised for robust development.
Growing Focus on Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity concerns are becoming paramount in the Global Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Industry. As vehicles become more connected, the risk of cyber threats increases, prompting manufacturers to prioritize the security of their software systems. OTA updates serve as a critical tool for addressing vulnerabilities and deploying security patches in real-time. This proactive approach to cybersecurity not only protects consumers but also enhances the overall integrity of automotive systems. As the industry grapples with evolving cyber threats, the emphasis on secure OTA solutions is likely to drive market growth, ensuring that manufacturers can safeguard their vehicles against potential attacks.
Consumer Awareness and Acceptance
Consumer awareness and acceptance of OTA updates are crucial drivers in the Global Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Industry. As consumers become more informed about the benefits of OTA technology, including convenience and enhanced vehicle performance, their willingness to embrace such updates increases. Educational initiatives by manufacturers and industry stakeholders play a vital role in shaping consumer perceptions and fostering acceptance. This growing awareness is expected to contribute to the market's expansion, as more consumers recognize the advantages of receiving timely software updates directly to their vehicles, thereby enhancing their overall driving experience.
Cost Efficiency and Reduced Downtime
Cost efficiency is a pivotal driver in the Global Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Industry. OTA updates allow manufacturers to deploy software fixes and enhancements without requiring physical dealership visits, thereby minimizing operational costs and reducing vehicle downtime. This capability is particularly advantageous in the context of recalls, where traditional methods can be cumbersome and expensive. By leveraging OTA technology, automakers can achieve significant savings and improve customer satisfaction. As the market evolves, it is anticipated that the cost benefits associated with OTA updates will further incentivize manufacturers to adopt this technology, contributing to a projected market growth to 35.3 USD Billion by 2035.
Increasing Demand for Connected Vehicles
The Global Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Industry is experiencing a surge in demand for connected vehicles, driven by consumer preferences for advanced technology and seamless connectivity. As vehicles become more integrated with smart technologies, manufacturers are compelled to implement OTA updates to enhance user experience and maintain competitive advantage. In 2024, the market is projected to reach 6.22 USD Billion, reflecting a growing recognition of the benefits of real-time software updates. This trend is likely to continue as consumers increasingly expect their vehicles to offer the same level of connectivity and functionality as their personal devices.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Enhancements
Regulatory compliance is increasingly influencing the Global Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Industry. Governments worldwide are imposing stricter regulations regarding vehicle safety and emissions, necessitating timely software updates to meet these standards. OTA updates enable manufacturers to quickly address compliance issues and enhance vehicle safety features without requiring physical recalls. This capability not only ensures adherence to regulations but also fosters consumer trust in automotive brands. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, the demand for OTA solutions that facilitate compliance is expected to rise, further propelling market growth.
Market Segment Insights
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Technology Insights
<p>Based on technology, the Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market segmentation includes firmware over-the-air [FOTA] and software over-the-air [SOTA]. The Software over-the-air (SOTA) segment has had the largest market share in the past few years. The growth of the automotive SOTA segment is expected to be mainly driven by growing infotainment applications such as live traffic updates, park assistance, e-mail applications, and social media apps.</p>
<p>Figure1: Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market, By Platform, 2024 & 2030 (USD billion)</p>
<p>Source: Secondary Research, Primary Research, Market Research Future Database, and Analyst Review</p>
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Application Insights
<p>Based on application, the Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market segmentation includes Electronic Control Unit (ECU), Infotainment, Safety & Security, and Telematics Control Unit (TCU), among others. The Telematics Control Unit (TCU) segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period due to the progress in the number of telecommunication applications. Numerous automotive manufacturers offer telematics control units as conventional devices in their vehicles.</p>
<p>July 2022: new cyber security law will be mandatory for all new vehicle types in the European Union, and from July 2024, all new cars manufactured. For instance, South Korea and Japan attempt to establish cyber security rules. Furthermore, the automotive industry is developing ISO/SAE 21434, Road vehicles – Cyber security engineering standard within the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The standard implementation is intended to assist manufacturers in keeping up with evolving technology and cyber-attack strategies.</p>
<p>Hence, cyber security regulations in the automotive sector are expected to fuel the growth of the global automotive OTA market during the forecast period.</p>
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Propulsion Insights
<p>Based on propulsion, the Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market data includes ICE, Electric vehicles. The ICE segment dominated the Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates market. This can be credited to cars and most medium- and heavy commercial vehicles powered by conventional engines. The electric category will witness faster growth, with a rate of 28%. This has much to do with government support, such as grants and initiatives, for the acceptance of EVs and the strict emission regulations. Furthermore, nearly all EVs are equipped with innovative connected systems for effective processes and high security and safety.</p>
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Vehicle Type Insights
<p>Based on vehicle type, the global automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates industry includes passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and heavy commercial vehicles. Passenger car segments dominated the market. Passenger vehicles had the larger share, of about 68%, and it will be like this in the future. It will be because of the growing sales of mid-range and premium passenger vehicles with added features, including autonomy. Moreover, Light Commercial Vehicle has numerous systems for virtual assistance, eye tracking, driver monitoring, speech recognition, gesture recognition, and natural language interfaces.</p>
<p>These systems rely on regular OTA updates for safe operation, further contributing to the market's growth.</p>
Get more detailed insights about Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Research Report - Global Forecast till 2030
Regional Insights
By Region, the study provides market insights into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World. North American automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market, due to the increasing number of connected car devices in vehicles, the rise in production of electric vehicles, and standard infotainment & telematics services updates will boost the market growth in this Region.
Further, the major countries studied in the market report are The U.S., Canada, German, France, the UK, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Brazil.
Figure2: Automotive Over-The-Air (Ota) Updates Market Share By Region 2022 (%)
Source: Secondary Research, Primary Research, Market Research Future Database, and Analyst Review
Europe's automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market accounts for the second-largest market share due to the increased penetration of internet services in the Region and the adoption of advanced technology. Further, the German automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market held the largest market share, and the UK automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market was the fastest-growing market in the European Region.
The Asia-Pacific automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2024 to 2030. This is due to major automotive manufacturers of countries, like China and India, in significant automotive hubs in the Region, which are anticipated to boost the procurements of automotive over-the-air (OTA) Updates Market. Moreover, China’s automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market held the largest market share. The Indian automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market was the fastest-growing market in the Asia-Pacific region.
Key Players and Competitive Insights
Leading market players are investing heavily in research and development to expand their product lines, which will help the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates to the market grow even more. Market participants are also undertaking various strategic activities to expand their global footprint, with important market developments including new product launches, contractual agreements, mergers and acquisitions, higher investments, and collaboration with other organizations. The Automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates industry must offer cost-effective items to expand and survive in a more competitive and rising market climate.
Manufacturing locally to minimize operational costs is one of the key business tactics manufacturers use in the global automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates industry to benefit clients and increase the market sector. The automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates industry has offered the military some of the most significant advantages in recent years.
Major players in the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates to market, including Robert Bosch GmbH, NXP Semiconductors N.V, Verizon Communications Inc., Continental AG, Infineon Technologies AG, Qualcomm Incorporated, Intel Corporation, HARMAN International, Airbiquity Inc, Aptiv, HERE Technologies, BlackBerry QNX Software Systems Limited, Garmin Ltd., Intellias Ltd., and others, are attempting to increase market demand by investing in research and development operations.
Qualcomm is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software, and services related to wireless technology. It owns patents critical to the 5G, 4G, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA, and WCDMA mobile communications standards. Qualcomm Technologies Inc, a subsidiary of Qualcomm Inc, had announced the expansion of 5G test networks. The expansion of networks included Over-the-air configuration for sub-6 GHz bands and millimeter waves.
Verizon Communications Inc., commonly known as Verizon, is an American multinational telecommunications conglomerate and a corporate component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The company is headquartered at 1095 Avenue of the Americas in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, but is incorporated in Delaware. Verizon had launched Hum, the first 4G LTE-connected solution for cars that came with built-in Google Assistant.
Key Companies in the Automotive Over The Air Updates Market market include






Industry Developments
NXP Semiconductors N.V.: January 2024: NXP Semiconductors was recognized as a major player in the automotive OTA updates market, reflecting its significant role in the industry.
Verizon Communications Inc.: January 2024: Verizon Communications Inc. was acknowledged as a key participant in the automotive OTA updates market, highlighting its involvement in advancing OTA technologies.
Infineon Technologies AG: January 2024: Infineon Technologies partnered with Aurora Labs to enhance automotive safety through AI-driven predictive maintenance OTA solutions. This collaboration combines Aurora Labs' Line-of-Code Intelligence™ technology with Infineon's AURIX™ TC4x microcontrollers to improve the reliability and safety of critical vehicle components.
Robert Bosch GmbH: May 2021: Bosch introduced the Bosch Software Update Service, an OTA platform designed to provide secure and scalable software updates to vehicles and other connected devices.
Continental AG: April 2021: Continental launched Continental OTA Plus, a solution aimed at enabling secure and efficient software updates for vehicles and other connected devices.
February 2019: Qualcomm Technologies Inc, a subsidiary of Qualcomm Inc, announced the expansion of 5G test networks. The expansion of networks included Over-the-air configuration for sub-6 GHz bands and millimeter waves.
January 2019: Verizon launched Hum, the first 4G LTE-connected solution for cars that came with built-in Google Assistant.
Future Outlook
Automotive Over The Air Updates Market Future Outlook
<p>The Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market is projected to grow at a 17.08% CAGR from 2024 to 2035, driven by increasing vehicle connectivity, demand for software updates, and enhanced cybersecurity measures.</p>
New opportunities lie in:
- <p>Develop advanced cybersecurity solutions to protect OTA systems from potential threats. Create partnerships with automotive manufacturers for seamless OTA integration. Invest in AI-driven analytics to personalize OTA update offerings for consumers.</p>
<p>By 2035, the market is expected to reach unprecedented levels, reflecting robust growth and innovation.</p>
Market Segmentation
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Regional Outlook
- {""=>["US"
- "Canada"]}
- {""=>["Germany"
- "France"
- "UK"
- "Italy"
- "Spain"
- "Rest of Europe"]}
- {""=>["China"
- "Japan"
- "India"
- "Australia"
- "South Korea"
- "Rest of Asia-Pacific"]}
- {""=>["Middle East"
- "Africa"
- "Latin America"]}
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Propulsion Outlook
- ICE
- Electric Vehicle
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Technology Outlook
- Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
- Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Application Outlook
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
- Infotainment
- Safety & Security
- Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
- others
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Vehicle Type Outlook
- Passenger Car
- Light Commercial Vehicle
- Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Report Scope
| Report Attribute/Metric | Details |
| Market Size 2022 | USD 4.5 billion |
| Market Size 2023 | USD 5.34 billion |
| Market Size 2030 | USD 14.95 billion |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) | 18.72% (2024-2030) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Market Forecast Period | 2024-2030 |
| Historical Data | 2019- 2022 |
| Market Forecast Units | Value (USD Billion) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
| Segments Covered | By Technology, By Application, By Propulsion, By Vehicle Type, and Region |
| Geographies Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World |
| Countries Covered | The U.S., Canada, German, France, the UK, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Brazil |
| Key Companies Profiled | Robert Bosch GmbH, NXP Semiconductors N.V, Verizon Communications Inc., Continental AG, Infineon Technologies AG, Qualcomm Incorporated, Intel Corporation, HARMAN International, Airbiquity Inc, Aptiv, HERE Technologies, BlackBerry QNX Software Systems Limited, Garmin Ltd., Intellias Ltd. |
| Key Market Opportunities | Government initiatives Development commercial sectors globally |
| Key Market Dynamics | With the rapid growth in connected cars globally, vehicles are becoming more software dependent. |
Market Highlights
Author
Latest Comments
This is a great article! Really helped me understand the topic better.
Thanks for sharing this. I’ve bookmarked it for later reference.
FAQs
How much is the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market?
The global automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates were valued at USD 4.5 Billion in 2022.
What is the growth rate of the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market?
The global market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.72% during the forecast period, 2024-2030.
Which Region held the largest market share in the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market?
North America had the largest share of the global market
Who are the key players in the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market?
The key players in the market are Robert Bosch GmbH, NXP Semiconductors N.V, Verizon Communications Inc., Continental AG, Infineon Technologies AG, Qualcomm Incorporated, Intel Corporation, HARMAN International, Airbiquity Inc, Aptiv, HERE Technologies, BlackBerry QNX Software Systems Limited, Garmin Ltd., and Intellias Ltd.
Which type led the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market?
The passenger car automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates category dominated the market in 2022.
Which Propulsion had the largest market share in the automotive over-the-air (OTA) updates market?
The ICE –based Propulsion had the largest share of the global market.
-
List of Tables and Figures
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Market Segmentation
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Technology Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Application Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Propulsion Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Vehicle Type Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Regional Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
North America Outlook(USD Billion, 2019-2030)
North America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
North America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
North America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
North America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
US Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
US Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
US Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
US Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
US Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
CANADA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
CANADA Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
CANADA Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
CANADA Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
CANADA Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Europe Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Europe Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Europe Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Europe Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Europe Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Germany Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Germany Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Germany Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Germany Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Germany Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
France Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
France Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
France Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
France Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
France Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
UK Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
UK Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
UK Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
UK Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
UK Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
ITALY Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
ITALY Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
ITALY Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
ITALY Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
ITALY Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
SPAIN Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Spain Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Spain Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Spain Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Spain Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Rest Of Europe Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Rest Of Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
REST OF Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Rest Of Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Rest Of Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Asia-Pacific Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
China Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
China Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
China Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
China Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
China Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Japan Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Japan Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Japan Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Japan Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Japan Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
India Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
India Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
India Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
India Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
India Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Australia Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Australia Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Australia Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Australia Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Australia Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Rest of Asia-Pacific Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Rest of Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Rest of Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Rest of Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Rest of Asia-Pacific Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Rest of the World Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Rest of the World Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Rest of the World Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Rest of the World Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Rest of the World Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Middle East Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Middle East Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Middle East Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Middle East Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Middle East Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Africa Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Africa Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Africa Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Africa Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Africa Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Latin America Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2030)
Latin America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Technology
Firmware Over-The-Air [FOTA]
Software Over-The-Air [SOTA]
Latin America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Application
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Infotainment
Safety & Security
Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
Others
Latin America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Propulsion
ICE
Electric Vehicle
Latin America Automotive Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Light Commercial Vehicle
Heavy Commercial Vehicle

Free Sample Request
Kindly complete the form below to receive a free sample of this Report
Customer Strories
“I am very pleased with how market segments have been defined in a relevant way for my purposes (such as "Portable Freezers & refrigerators" and "last-mile"). In general the report is well structured. Thanks very much for your efforts.”
Leave a Comment