

- Global Market Outlook
- In-depth analysis of global and regional trends
- Analyze and identify the major players in the market, their market share, key developments, etc.
- To understand the capability of the major players based on products offered, financials, and strategies.
- Identify disrupting products, companies, and trends.
- To identify opportunities in the market.
- Analyze the key challenges in the market.
- Analyze the regional penetration of players, products, and services in the market.
- Comparison of major players’ financial performance.
- Evaluate strategies adopted by major players.
- Recommendations
- Vigorous research methodologies for specific market.
- Knowledge partners across the globe
- Large network of partner consultants.
- Ever-increasing/ Escalating data base with quarterly monitoring of various markets
- Trusted by fortune 500 companies/startups/ universities/organizations
- Large database of 5000+ markets reports.
- Effective and prompt pre- and post-sales support.
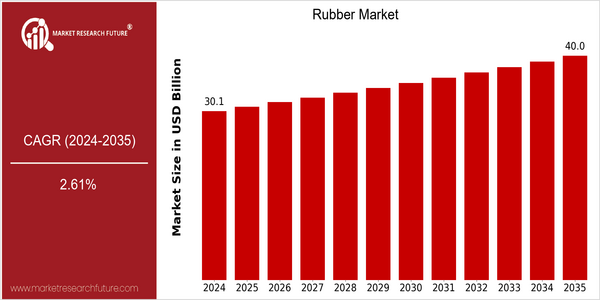
Market Size Snapshot
| Year | Value |
|---|---|
| 2024 | USD 30.14 Billion |
| 2035 | USD 40.0 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 2.61 % |
Note – Market size depicts the revenue generated over the financial year
The global rubber market is poised for steady growth, with a current market size of USD 30.14 billion in 2024, projected to reach USD 40.0 billion by 2035. This growth trajectory reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.61% from 2025 to 2035. The market's expansion can be attributed to several key factors, including the increasing demand for rubber in various end-use industries such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods, which are driving the need for innovative rubber products and applications. Technological advancements in rubber processing and the development of synthetic rubber alternatives are also contributing to market growth. Companies are investing in research and development to enhance the performance characteristics of rubber, making it more suitable for diverse applications. For instance, major players like Bridgestone Corporation and Michelin are focusing on sustainable practices and product innovation, including the launch of eco-friendly tires and partnerships aimed at improving supply chain efficiency. These strategic initiatives not only bolster their market position but also align with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products, further fueling the rubber market's growth.
Regional Market Size
Regional Deep Dive
The Rubber Market is characterized by diverse dynamics across different regions, influenced by local demand, production capabilities, and regulatory frameworks. In North America, the market is driven by a robust automotive industry and increasing demand for sustainable rubber products. Europe showcases a strong emphasis on innovation and eco-friendly materials, while Asia-Pacific remains the largest producer and consumer, benefiting from rapid industrialization and urbanization. The Middle East and Africa are witnessing growth due to infrastructural developments, and Latin America is focusing on expanding its agricultural applications of rubber.
Europe
- Europe is leading in the development of smart rubber materials, with organizations like the European Rubber Industry Association (ERIA) promoting research and collaboration among key players to enhance product performance.
- The EU's Green Deal is influencing the rubber market by encouraging the use of recycled materials, which is expected to drive innovation and sustainability in the industry.
Asia Pacific
- Asia-Pacific is witnessing significant investments in rubber plantations, particularly in countries like Thailand and Vietnam, driven by the increasing demand for natural rubber in various industries.
- The region is also seeing advancements in technology, with companies like Bridgestone and Continental developing high-performance tires that utilize advanced rubber compounds to improve fuel efficiency and safety.
Latin America
- Latin America is focusing on the agricultural applications of rubber, with countries like Brazil investing in research to enhance the yield and quality of rubber trees, which is expected to improve local economies.
- The region is also experiencing a rise in small-scale rubber producers, supported by government programs aimed at promoting sustainable farming practices and increasing local employment opportunities.
North America
- The North American rubber market is experiencing a shift towards sustainable practices, with companies like Goodyear and Michelin investing in bio-based rubber alternatives to meet consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
- Regulatory changes, such as the EPA's stricter emissions standards, are pushing manufacturers to innovate and adopt cleaner production processes, which is expected to enhance the market's growth potential.
Middle East And Africa
- In the Middle East, the rubber market is being bolstered by government initiatives aimed at enhancing infrastructure, with projects like the UAE's Vision 2021 promoting the use of rubber in construction materials.
- Africa is seeing a rise in local rubber production, with initiatives from organizations like the African Rubber Association aimed at boosting sustainable practices and increasing the region's competitiveness in the global market.
Did You Know?
“Did you know that approximately 70% of the world's natural rubber is produced in Southeast Asia, with Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia being the top three producers?” — International Rubber Study Group
Segmental Market Size
The rubber market segment, particularly natural rubber, plays a crucial role in various industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods. This segment is currently experiencing stable growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly materials and advancements in synthetic rubber technologies. Key factors propelling this demand include the rising need for durable and sustainable products, regulatory policies promoting green materials, and technological innovations enhancing rubber processing methods. Currently, the adoption of natural rubber is in a mature stage, with leading companies like Michelin and Bridgestone implementing sustainable sourcing practices in regions such as Southeast Asia. Primary applications include tire manufacturing, where natural rubber is favored for its superior elasticity and strength, and in medical supplies, where biocompatibility is essential. Trends such as the push for sustainability and government mandates on emissions are accelerating growth in this segment. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies and bio-based rubber production methods are shaping the future landscape of the rubber market.
Future Outlook
The Rubber Market is poised for steady growth from 2024 to 2035, with a projected market value increase from $30.14 billion to $40.0 billion, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.61%. This growth trajectory is underpinned by rising demand across various sectors, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods, where rubber is integral for manufacturing tires, seals, and other essential components. As global vehicle production is expected to rise, particularly in emerging markets, the automotive sector will continue to be a significant driver of rubber consumption, with usage rates anticipated to increase by approximately 3% annually in this segment alone. Key technological advancements, such as the development of sustainable rubber alternatives and enhanced production processes, are expected to reshape the market landscape. Innovations in synthetic rubber production, driven by environmental policies and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products, will likely gain traction. Additionally, the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is anticipated to create new opportunities for rubber manufacturers, as these vehicles require specialized tires and components. As the market evolves, stakeholders must remain agile, adapting to regulatory changes and shifting consumer demands to capitalize on the growth potential in the rubber industry.
Covered Aspects:| Report Attribute/Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Growth Rate | 5.20% (2023-2032) |
Rubber Market Highlights:
Leading companies partner with us for data-driven Insights
Kindly complete the form below to receive a free sample of this Report
Tailored for You
- Dedicated Research on any specifics segment or region.
- Focused Research on specific players in the market.
- Custom Report based only on your requirements.
- Flexibility to add or subtract any chapter in the study.
- Historic data from 2014 and forecasts outlook till 2040.
- Flexibility of providing data/insights in formats (PDF, PPT, Excel).
- Provide cross segmentation in applicable scenario/markets.









