Market Growth Projections
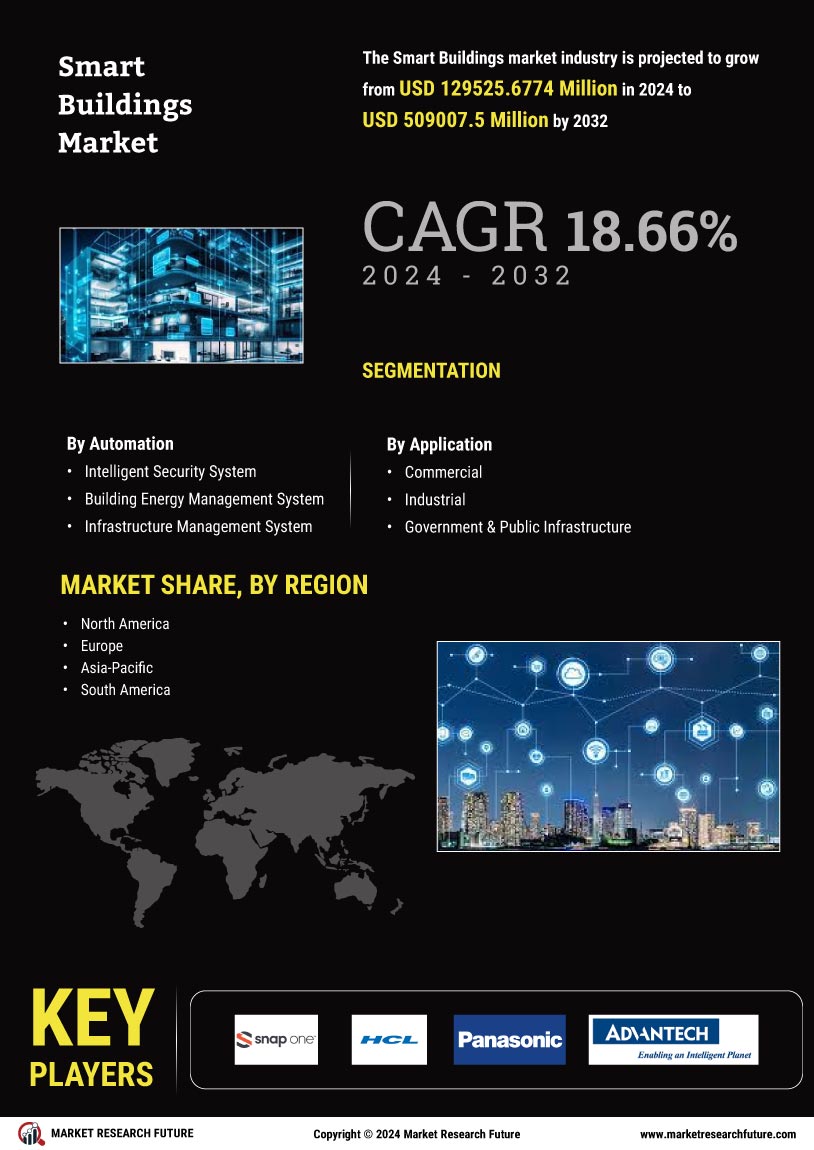
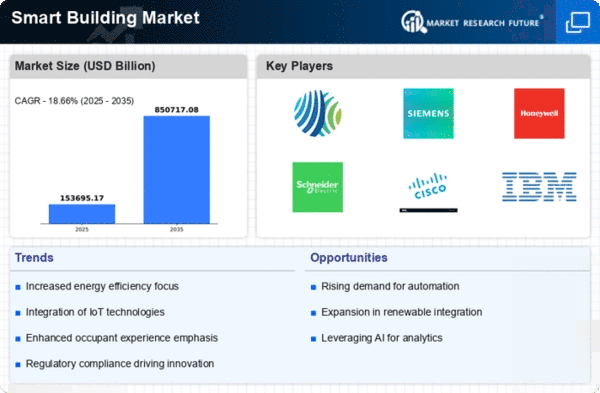
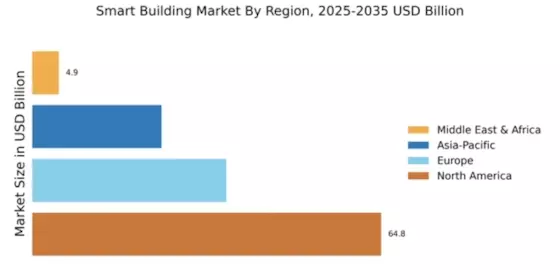
The Global Smart Buildings Market Industry is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. With a market value of 83.5 USD Billion in 2024, it is anticipated to reach 427.3 USD Billion by 2035. This growth trajectory indicates a compound annual growth rate of 16.0% from 2025 to 2035. Such projections highlight the increasing adoption of smart technologies in buildings, driven by factors such as energy efficiency, sustainability, and technological advancements. As the market evolves, stakeholders are likely to explore new opportunities and innovations to meet the demands of a rapidly changing environment.
Increased Focus on Sustainability
The Global Smart Buildings Market Industry is witnessing a heightened focus on sustainability as environmental concerns gain prominence. Building owners and developers are increasingly prioritizing sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and implementing green building materials. This shift is driven by both consumer demand and regulatory pressures. For example, LEED certification has become a benchmark for sustainable building practices, encouraging the integration of smart technologies that enhance energy efficiency. As sustainability becomes a key consideration in building design and operation, the market for smart buildings is likely to expand significantly.
Rising Demand for Energy Efficiency
The Global Smart Buildings Market Industry experiences a notable surge in demand for energy-efficient solutions. As energy costs continue to rise, building owners increasingly seek technologies that optimize energy consumption. Smart buildings utilize advanced sensors and automation systems to monitor and control energy usage, leading to significant cost savings. For instance, the implementation of smart lighting and HVAC systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. This trend is expected to contribute to the market's growth, with projections indicating a market value of 83.5 USD Billion in 2024 and a remarkable increase to 427.3 USD Billion by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 16.0% from 2025 to 2035.
Government Initiatives and Regulations
Government initiatives and regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the Global Smart Buildings Market Industry. Many countries are implementing stringent building codes and standards aimed at enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. For example, the European Union has set ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions, which encourages the adoption of smart building technologies. Such regulations not only promote energy-efficient practices but also provide financial incentives for building owners to invest in smart technologies. This regulatory landscape is likely to drive market growth, as compliance with these standards becomes increasingly essential for new constructions and renovations.
Technological Advancements in IoT and AI
Technological advancements in the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the Global Smart Buildings Market Industry. The integration of IoT devices enables real-time monitoring and control of building systems, enhancing operational efficiency. AI algorithms analyze data collected from various sensors to optimize building performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve occupant comfort. For instance, smart thermostats can learn user preferences and adjust heating and cooling accordingly, leading to energy savings. As these technologies continue to evolve, their adoption in smart buildings is expected to accelerate, further fueling market growth.
Growing Urbanization and Population Density
The Global Smart Buildings Market Industry is significantly influenced by the trends of growing urbanization and increasing population density. As urban areas expand, the demand for efficient and technologically advanced buildings rises. Smart buildings offer solutions to manage resources effectively in densely populated environments, addressing challenges such as energy consumption, waste management, and security. For instance, smart waste management systems can optimize collection routes based on real-time data, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This urbanization trend is expected to drive the market forward, as cities seek innovative solutions to accommodate their growing populations.