Increased Demand for Soil Amendment
The Europe biochar woody biomass market is experiencing a notable surge in demand, primarily attributed to the increased need for soil amendment. This growing demand is driven by several factors that underline the critical role biochar derived from woody biomass plays in enhancing soil quality and agricultural sustainability across the region. One of the primary drivers fueling the heightened interest in biochar as a soil amendment is the growing awareness of its profound benefits among both agricultural practitioners and environmental advocates.
Biochar, a highly porous, carbon-rich material produced through the pyrolysis of woody biomass, serves as an effective means to enhance soil fertility and structure. By integrating biochar into agricultural practices, farmers can significantly improve soil water retention, nutrient availability, and overall productivity. This increase in agricultural productivity is particularly appealing in Europe, where sustainable farming practices and food security are of paramount importance. In recent years, Europe has witnessed an amplified focus on sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation. Biochar from woody biomass aligns perfectly with these priorities by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, sequestering carbon, and improving soil health.
As environmental concerns continue to gain momentum, policymakers and agricultural stakeholders are increasingly recognizing the potential of biochar as a powerful tool for mitigating climate change and preserving natural ecosystems. Furthermore, the rising demand for organic and sustainable food production methods in Europe is contributing to the heightened interest in biochar as a soil amendment. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the quality and origin of their food, which has driven a shift towards environmentally friendly farming practices.
Biochar's ability to enhance soil conditions and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers aligns with this trend, making it an attractive choice for farmers looking to meet the growing demand for organic and sustainably grown produce. The need for sustainable land management practices is also intensifying due to the increasing threat of soil degradation and erosion, which are adversely affecting agricultural yields. Biochar acts as a long-term soil conditioner, preventing nutrient leaching and erosion by improving soil structure and stability.
European farmers are recognizing the importance of mitigating these soil-related challenges to maintain consistent crop yields, which has led to a growing demand for biochar to address these pressing issues. Furthermore, research and development efforts in the field of biochar production and application are advancing, offering innovative solutions and enhancing the market's appeal. This includes the development of tailored biochar blends and formulations to address specific soil types and crop requirements, further driving the demand for these products.
As Europe works towards achieving its sustainability goals, biochar derived from woody biomass is increasingly seen as a valuable asset in achieving these objectives. Governments and institutions are providing incentives and support for the adoption of biochar in agriculture, further propelling its use as a soil amendment. In conclusion, the Europe biochar woody biomass market is witnessing a substantial surge in demand, with the increased need for soil amendment emerging as a prominent driver. The remarkable benefits of biochar in improving soil quality, boosting agricultural productivity, and mitigating environmental challenges have spurred its adoption in European agriculture.
As the region continues to prioritize sustainable farming practices and environmental conservation, the biochar market is poised for sustained growth, providing a promising solution to the pressing issue of soil amendment.
Growing Interest in Carbon Sequestration
The European Biochar Woody Biomass Market is experiencing a significant surge in interest and activity due to the growing recognition of carbon sequestration as a critical tool in mitigating climate change. Carbon sequestration through the utilization of biochar, a type of charcoal produced from woody biomass, has become a focal point in the region's efforts to address environmental concerns. Europe's commitment to combatting climate change is evident in its adoption of ambitious sustainability and carbon reduction goals, such as the European Green Deal and the Paris Agreement.
As part of this broader strategy, there is an increasing emphasis on finding innovative and sustainable solutions to capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Biochar, a charcoal-like material obtained from the pyrolysis of woody biomass, is emerging as a promising method for carbon sequestration. One key driver for this growing interest in carbon sequestration through biochar lies in its exceptional ability to enhance soil health and promote carbon retention in the ground. By integrating biochar into agricultural practices, Europe aims to improve soil fertility, water retention, and overall crop yields.
This not only bolsters the agricultural sector but also contributes to carbon storage in the long term. European farmers and landowners are increasingly adopting biochar as an eco-friendly and sustainable approach to bolstering the continent's agricultural resilience and combating land degradation. Another significant factor propelling the biochar woody biomass market's growth is the increasing recognition of its potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Utilizing woody biomass to produce biochar allows for the removal of carbon from the atmosphere and the prevention of its release during biomass decomposition. By channeling this carbon into biochar, Europe is taking strides towards achieving its net-zero emission goals. Various industries, including agriculture, forestry, and even waste management, are actively exploring biochar as a means of carbon sequestration, thereby reducing their carbon footprint and supporting a greener, more sustainable future. Furthermore, the European biochar market is being driven by robust research and development efforts.
Scientists, policymakers, and industry stakeholders are working collaboratively to explore the best practices for producing and using biochar. This includes optimizing production methods, understanding the impact on various soil types, and assessing the overall environmental benefits. With increased funding and support for research initiatives, Europe is poised to unlock the full potential of biochar as a powerful carbon sequestration tool. The European Union's dedication to fostering a circular and sustainable bioeconomy is yet another influential factor in the rise of biochar made from woody biomass.
Biochar production not only diverts organic waste from landfills but also creates new revenue streams, contributing to a more circular and sustainable economy. The potential for job creation and economic growth is also a significant driver behind this trend. In conclusion, the growing interest in carbon sequestration through biochar derived from woody biomass in the European market is underpinned by a confluence of factors.
Europe's commitment to climate change mitigation, its focus on soil health and agriculture, efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, robust research and development activities, and the promotion of a circular bioeconomy are all contributing to the surging demand for biochar. As the region continues to emphasize sustainability and environmental responsibility, the biochar woody biomass market is poised for sustained growth, offering a promising solution to address the challenges of climate change and carbon management.
Renewable Energy Policy Drive Biochar Woody Biomass Market Expansion
Renewable energy policies are at the forefront of driving the expansion of the biochar woody biomass market in Europe. As the continent seeks to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the impacts of climate change, biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from the pyrolysis of woody biomass, has emerged as a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution. European governments have adopted a range of policies and incentives to encourage the production and use of biochar as a means to achieve their renewable energy and carbon sequestration goals.
In addition to energy policies, biochar's potential to improve soil health and agricultural productivity plays a vital role in driving market expansion. The European Union's Common Agricultural Policy promotes sustainable land management practices, and biochar can enhance soil structure, nutrient retention, and water-holding capacity. As a result, farmers and agricultural stakeholders are increasingly turning to biochar as a means to meet these sustainability requirements. Moreover, biochar's carbon sequestration properties can enable farmers to participate in carbon credit programs, adding an economic incentive for its adoption.
The growing awareness of the environmental and economic benefits of biochar also extends to research and innovation.
European universities and research institutions are actively studying biochar's applications and exploring ways to optimize its production processes. Collaborations between the public and private sectors further accelerate technological advancements and market expansion. This synergistic relationship between research, innovation, and policy development creates a robust ecosystem that supports the biochar woody biomass market's growth. In conclusion, renewable energy policies, combined with the broader sustainability and circular economy initiatives in Europe, are the primary drivers behind the expanding biochar woody biomass market.
The commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving soil health, and repurposing waste biomass aligns with the multifaceted benefits of biochar. As governments and stakeholders increasingly recognize its potential, the biochar market is poised for substantial growth, offering a promising path toward a greener and more sustainable future for Europe.
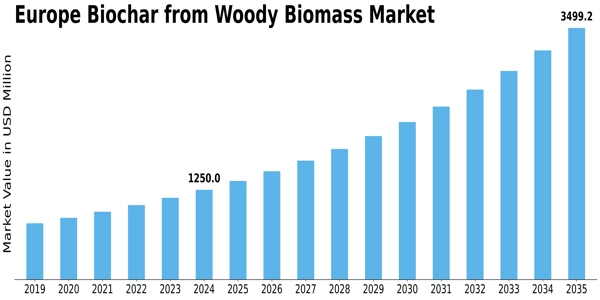
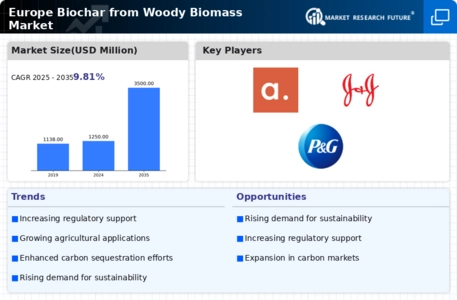
<p>The increasing emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices and carbon sequestration is likely to drive the demand for biochar derived from woody biomass across Europe.</p>
European Commission





Leave a Comment