Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
North America
Europe
South America
Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
North America Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
North America Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
North America Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
North America Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
North America Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
North America Anticoagulation Market by Regional Type
US
Canada
US Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
US Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
US Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
US Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
US Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
CANADA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
CANADA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
CANADA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
CANADA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
CANADA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
Europe Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
Europe Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
Europe Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
Europe Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
Europe Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
Europe Anticoagulation Market by Regional Type
Germany
UK
France
Russia
Italy
Spain
Rest of Europe
GERMANY Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
GERMANY Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
GERMANY Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
GERMANY Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
GERMANY Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
UK Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
UK Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
UK Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
UK Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
UK Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
FRANCE Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
FRANCE Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
FRANCE Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
FRANCE Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
FRANCE Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
RUSSIA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
RUSSIA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
RUSSIA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
RUSSIA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
RUSSIA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
ITALY Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
ITALY Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
ITALY Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
ITALY Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
ITALY Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
SPAIN Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
SPAIN Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
SPAIN Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
SPAIN Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
SPAIN Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
REST OF EUROPE Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
REST OF EUROPE Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
REST OF EUROPE Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
REST OF EUROPE Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
REST OF EUROPE Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
APAC Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
APAC Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
APAC Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
APAC Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
APAC Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
APAC Anticoagulation Market by Regional Type
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Malaysia
Thailand
Indonesia
Rest of APAC
CHINA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
CHINA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
CHINA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
CHINA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
CHINA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
INDIA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
INDIA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
INDIA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
INDIA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
INDIA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
JAPAN Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
JAPAN Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
JAPAN Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
JAPAN Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
JAPAN Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
SOUTH KOREA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
SOUTH KOREA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
SOUTH KOREA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
SOUTH KOREA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
SOUTH KOREA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
MALAYSIA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
MALAYSIA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
MALAYSIA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
MALAYSIA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
MALAYSIA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
THAILAND Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
THAILAND Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
THAILAND Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
THAILAND Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
THAILAND Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
INDONESIA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
INDONESIA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
INDONESIA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
INDONESIA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
INDONESIA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
REST OF APAC Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
REST OF APAC Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
REST OF APAC Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
REST OF APAC Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
REST OF APAC Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
South America Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
South America Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
South America Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
South America Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
South America Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
South America Anticoagulation Market by Regional Type
Brazil
Mexico
Argentina
Rest of South America
BRAZIL Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
BRAZIL Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
BRAZIL Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
BRAZIL Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
BRAZIL Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
MEXICO Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
MEXICO Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
MEXICO Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
MEXICO Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
MEXICO Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
ARGENTINA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
ARGENTINA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
ARGENTINA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
ARGENTINA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
ARGENTINA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
MEA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
MEA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
MEA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
MEA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
MEA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
MEA Anticoagulation Market by Regional Type
GCC Countries
South Africa
Rest of MEA
GCC COUNTRIES Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
GCC COUNTRIES Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
GCC COUNTRIES Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
GCC COUNTRIES Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
GCC COUNTRIES Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
SOUTH AFRICA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
SOUTH AFRICA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
SOUTH AFRICA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
SOUTH AFRICA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
SOUTH AFRICA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics
REST OF MEA Outlook (USD Billion, 2019-2035)
REST OF MEA Anticoagulation Market by Drug Type
Vitamin K Antagonists
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Heparin
REST OF MEA Anticoagulation Market by Route of Administration Type
Oral
Injectable
Transdermal
REST OF MEA Anticoagulation Market by Indication Type
Atrial Fibrillation
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pulmonary Embolism
Myocardial Infarction
REST OF MEA Anticoagulation Market by End Use Type
Hospitals
Home Care
Clinics

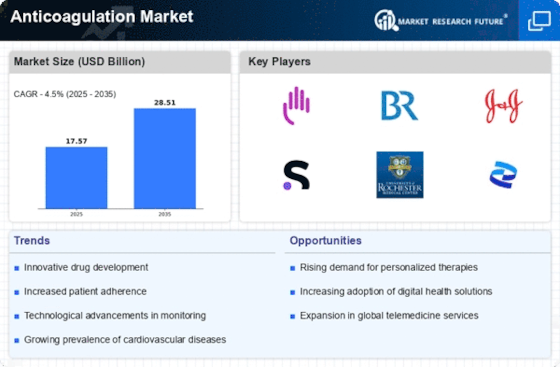















Leave a Comment