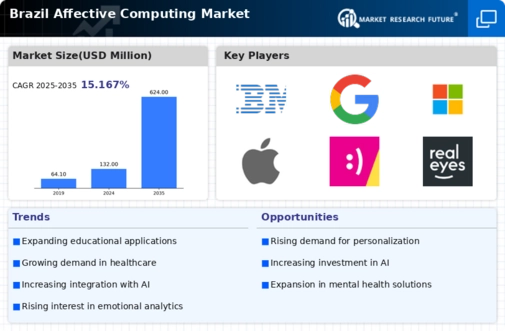
The Brazil Affective Computing Market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology that allow machines to recognize and interpret human emotions. This segment is becoming increasingly crucial across various industries, such as healthcare, education, and customer service, where understanding and processing human emotions can enhance user experience and operational efficiency. As businesses in Brazil aim to leverage the power of emotional insights to foster better interactions with consumers, numerous players are entering the market, each bringing unique strengths and offerings to capture the attention of stakeholders. To thrive in this competitive environment, companies must continuously innovate and adapt their strategies to meet the evolving needs of consumers while addressing the unique cultural and social dynamics present in Brazil.
IBM's regional research laboratories in São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, its first in South America, are the foundation of the company's strong presence in Brazil. There, work is being done on engagement systems, social data analytics, and natural resource solutions. The infrastructure and analytical skills these labs develop provide a strong basis for affective computing applications, ranging from context-driven healthcare solutions to sentiment-aware customer service, even though they aren't just focused on emotion AI. With its Watson platform, which integrates emotion and tone analysis across multiple industries, IBM dominates the global market for affective computing. IBM is well-positioned to develop and expand emotion-aware solutions in Brazil because of its leadership, specialized research presence, and enterprise ties.
Google uses its cloud infrastructure and worldwide AI experience to influence the affective computing market, notably in Brazil. Developers throughout the world, including those in Brazilian markets, may create emotion-aware apps with its Cloud Vision API's facial detection and emotion identification features. Google's inclusion among major worldwide market participants and its ongoing development of sympathetic AI features (such as improved emotion skills in virtual assistants) suggest a strategic footprint that extends to Latin America, even though particular initiatives aimed at Brazil aren't explicitly recorded. Google gives Brazilian developers and businesses the resources they need to embrace and localize affective computing solutions through its infrastructure, research output, and ethical AI focus.