Market Analysis
Floating Wind Turbine Market (Global, 2024)
Introduction
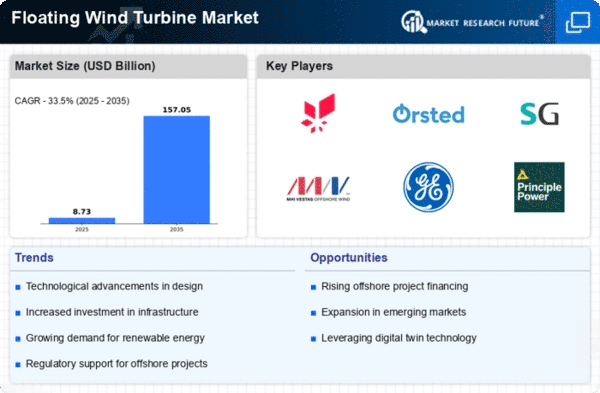
Floating wind-power is playing a major role in the transition to renewable energy sources. It is driven by the increasing demand for sustainable energy and the need to harness offshore wind resources. The limitations imposed by the depth of water on the use of conventional wind-power plants are being overcome by floating wind-power, which is enabling the placement of wind-turbines in previously inaccessible locations. This new technology is not only increasing the potential for wind-power but also reducing the negative impact on the environment and the disruption to the natural environment. It is a technology that is rapidly developing and which is attracting strategic alliances and significant investment. It is designed to increase the efficiency and reliability of floating wind-power systems. This is a technology that is transforming the energy industry. As energy companies become aware of the potential of floating wind-power to help meet energy and climate goals, the market is changing, bringing both challenges and opportunities.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- In 2024, the floating wind-turbine market will be dominated by government policies for the promotion of alternative energy. For example, the European Union has set itself the goal of achieving 40 per cent of its energy from renewable sources by 2030. This will require a budget of 1 0 billion. The United States, too, has introduced tax incentives such as the investment tax credit (ITC), which provides a 30 per cent tax credit for offshore wind-power projects, thus encouraging the development of floating wind-power technology.
- Economic
- The year 2024 is characterized by an increase in investment in the energy infrastructure of the future. For example, in the United Kingdom, the government has set aside one hundred and sixty million pounds for the development of offshore wind energy, including floating windmills. In addition, by 2025 the offshore wind energy industry is expected to create up to two hundred thousand jobs worldwide, of which a large part will be in the floating windmill sector. This shows the enormous potential of this market.
- Social
- In 2024 the public opinion and social acceptance of floating wind-turbines are growing more and more favourable. In Europe 75% of the inhabitants of the coastal regions are in favour of the construction of offshore wind-turbines, recognizing the possibilities for a clean and local production of energy. Education and information have also had an effect on public opinion, resulting in a ten per cent increase in public awareness of the advantages of floating wind-turbines over the past year.
- Technological
- The development of the wind power is important for the floating wind-power industry. The new inventions will bring more efficiency and lower costs. By 2024, the average capacity of the floating wind-turbines will reach 10 megawatts, and some prototypes will exceed this capacity. By developing new materials and new designs for the floating platforms, the costs will fall by a further 15 per cent, making the offshore wind-power industry more competitive.
- Legal
- The legal framework for floating windmills is evolving. New regulations are being introduced to make the permitting procedure more flexible. In 2024 the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management issues ten new offshore wind leases covering more than a million acres of federal waters. These changes in the law are crucial for the development of the floating windmill market and for ensuring that the environment is protected.
- Environmental
- In the year 2024, considerations of the environment are at the top of the list of floating windmills. Floating windmills are expected to reduce the annual emissions of carbon dioxide by an estimated 500,000 tons per project, which will help to achieve the world's climate goals. In addition, the mandatory requirement for an environment study for all new projects ensures that marine ecosystems are protected, which has led to a threefold increase in the monitoring of marine species in offshore wind farms.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- Medium - The floating wind turbine market is experiencing growth, attracting new players. However, high capital requirements, technological expertise, and regulatory hurdles create barriers to entry that limit the threat from new entrants.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- “The supply chain for floating wind-power plants includes a number of components such as the wind-turbine, moorings, and installation services. The increasing number of suppliers and manufacturers means that the bargaining power of suppliers is weakened.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- The buyers in the floating wind-power market, including government agencies and energy companies, have some negotiating power because of the availability of alternative energy sources. The specialized nature of the floating wind-power technology, however, limits their options, thus balancing the power equation.
- Threat of Substitutes
- As a unique solution for offshore energy production, other renewable energy sources, such as offshore wind, solar, and traditional energy sources, pose a moderate threat as substitutes, especially as technology advances.
- Competitive Rivalry
- High - The floating wind turbine market is characterized by intense competition among established players and new entrants. Companies are investing heavily in R&D to innovate and reduce costs, leading to a highly competitive environment.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- High energy efficiency and output compared to traditional wind turbines.
- Ability to harness wind energy in deeper waters where conventional turbines cannot operate.
- Growing technological advancements leading to reduced costs and improved performance.
Weaknesses
- High initial capital investment and installation costs.
- Technical challenges related to maintenance and durability in harsh marine environments.
- Limited infrastructure and supply chain for floating turbine components.
Opportunities
- Increasing global demand for renewable energy sources and sustainability initiatives.
- Government incentives and subsidies promoting offshore wind energy projects.
- Potential for innovation in turbine design and energy storage solutions.
Threats
- Intense competition from other renewable energy sectors, such as solar and onshore wind.
- Regulatory challenges and environmental concerns regarding marine ecosystems.
- Economic fluctuations that could impact investment in renewable energy projects.
Summary
Floating Wind Turbine Market is characterized by high energy efficiency and the ability to operate in deeper waters, which will help to position the market favorably in the context of the renewable energy market. The market, however, is hampered by the high initial cost and technical challenges. Opportunities exist for this market in the form of increasing demand for clean energy and supportive government policies. However, the market faces threats from competition and regulatory challenges. Strategic focus on innovation and cost reduction will be critical for market players to take advantage of opportunities and mitigate risks.


















Leave a Comment