Market Analysis
India Automotive Industry (Global, 2025)
Introduction
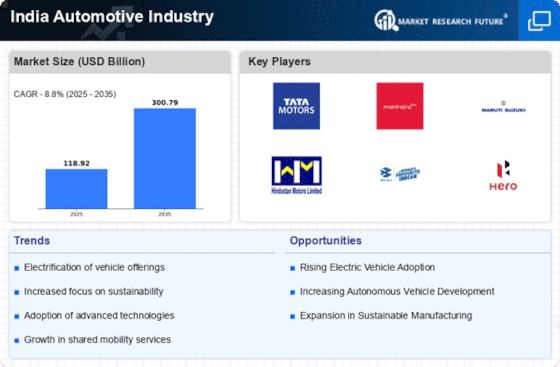
The India Automotive Industry stands as a pivotal sector within the nation's economy, characterized by its dynamic growth and transformative potential. As a hub for both manufacturing and innovation, the industry encompasses a diverse range of vehicles, including passenger cars, commercial vehicles, two-wheelers, and electric vehicles, reflecting the evolving preferences of consumers and the increasing emphasis on sustainability. The landscape is shaped by a confluence of factors such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer behaviors, all of which are driving the industry towards a more competitive and environmentally conscious future. With a burgeoning middle class and rising disposable incomes, the demand for personal mobility solutions is expected to intensify, prompting manufacturers to adapt their strategies to meet the needs of a diverse customer base. Furthermore, the push for electric mobility and the integration of smart technologies are set to redefine the automotive experience, positioning India as a key player in the global automotive arena. This report delves into the intricacies of the India Automotive Industry, exploring the current trends, challenges, and opportunities that will shape its trajectory in the coming years.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- In 2025, the Indian government is expected to spend around 15,400 billion to develop electric vehicle (EV) charging stations as part of its sustainable transport initiative. This investment is in line with the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which aims to promote the adoption of EVs in the country. By 2030, the government wants to achieve a goal of having 30 percent of vehicles on Indian roads to be electric vehicles. This will have a significant impact on the strategies and operations of the automobile industry.
- Economic
- By 2025, the automobile industry is expected to contribute to the GDP of the country by $ 750 billion. The industry is also expected to create employment directly and indirectly for 10 million people, mainly due to the increase in the manufacturing, sales and service sector. By then, the average salary of the employees of the automobile industry is expected to rise to $ 50,000 per year, which is a sign of the positive trend in employment and consumption.
- Social
- By 2025, the Indian automobile market is expected to have changed drastically, with the preference of more than half of the buyers being for eco-friendly vehicles. The change is attributed to the growing awareness of the middle class and the growing middle class, which is increasingly becoming interested in the environment. The urban population is also expected to increase from the present 330 million to 600 million. The demand for personal vehicles is expected to rise, and a trend towards shared mobility will influence the types of vehicles produced and sold.
- Technological
- Research and development in the Indian automobile industry is expected to touch 300 billion rupees by 2025. By then, connected vehicles and driverless cars are expected to be commonplace. This investment is essential if India is to become a hub for automobile innovation. More than half the automobile manufacturers are expected to use artificial intelligence and machine learning in their manufacturing processes. The integration of 5G technology is expected to enhance vehicle connectivity, thereby improving road safety and enhancing the efficiency of traffic.
- Legal
- The government of India has laid down new rules for the automobile industry in the country. By 2025, the automobile industry will have to comply with the Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) norms, which stipulate a reduction in nitrogen-oxide emissions by 70 per cent for diesel vehicles and 25 per cent for petrol vehicles. The government has estimated that this would require a substantial investment of about $2 billion by the industry to bring its production line and technology up to the required standards. In addition, the implementation of the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019, would affect vehicle registration and road safety standards.
- Environmental
- The Indian automobile industry is expected to face increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, with the government setting a target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 33 to 35% by 2030, compared to the level in 2005. The target is in line with India’s commitment under the Paris Agreement. It is estimated that the industry will need to invest around $120 billion by 2025 to meet these goals, which will also be driven by consumer demand for cleaner vehicles.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- The threat of new entrants to the Indian automobile industry in 2025 is expected to be moderate. High entry barriers such as high capital investment, stringent regulations and established brand loyalty among consumers are expected to act as deterrents. However, technological advancements and the emergence of electric vehicles may attract new entrants, particularly start-ups.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Suppliers in the motor industry have a moderate power of bargaining. The number of suppliers of the various parts is very large, but the tendency to vertical integration and the concentration of suppliers is giving some of them more power. The onset of electric vehicles is changing the supplier situation because it is bringing with it the need for new materials and technology, and thus influencing the power of bargaining.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- High The bargaining power of Indian consumers in the car market will be high in 2025. The availability of many brands will mean that consumers can easily change to another brand, which will lead to fierce competition among the manufacturers. The awareness of the importance of energy efficiency and the growing demand for fuel-efficient cars will also mean that consumers will be able to demand better features and better prices.
- Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of substitutes in the automobile industry is moderate. The demand for cars is still strong. Although they are facing competition from public transport, ride-hailing and electric bicycles, the demand for private cars remains strong. However, as urbanization continues and concerns over the environment grow, the demand for substitutes may grow, which will force the industry to keep innovating.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Competition in the Indian automobile industry is expected to be intense in 2025. Competition is expected to be fierce with the presence of many established and new players vying for market share. This will lead to intense price competition and aggressive marketing strategies. The rapid evolution of technology, especially in the field of electric and driverless cars, will also lead to intense competition, as companies will have to differentiate themselves to grab consumers’ attention.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Large consumer base with increasing disposable income.
- Strong manufacturing capabilities and skilled workforce.
- Government initiatives promoting electric vehicles and sustainability.
- Diverse automotive market including two-wheelers, passenger cars, and commercial vehicles.
- Growing investment in research and development for innovative technologies.
Weaknesses
- Infrastructure challenges, including inadequate road networks in some regions.
- High dependency on imports for certain components and raw materials.
- Regulatory hurdles and complex taxation systems.
- Limited penetration of electric vehicles compared to traditional fuel vehicles.
- Environmental concerns and pollution issues affecting public perception.
Opportunities
- Expansion of electric vehicle market driven by government incentives.
- Rising demand for connected and autonomous vehicle technologies.
- Potential for growth in export markets due to competitive manufacturing costs.
- Increased focus on sustainable and green technologies.
- Partnerships with tech companies for innovation in mobility solutions.
Threats
- Intense competition from global automotive players.
- Economic fluctuations impacting consumer purchasing power.
- Rapid technological changes requiring constant adaptation.
- Potential trade barriers and geopolitical tensions affecting supply chains.
- Regulatory changes related to emissions and safety standards.
Summary
India’s auto industry is expected to grow rapidly by 2025, backed by its large population and manufacturing strength. It will have to overcome obstacles such as the lack of skilled labor and regulatory complexities. Opportunities abound in electric vehicles and technological advancements, but the industry will have to cope with intense competition and macroeconomic uncertainties. The industry must focus on innovation, sustainability, and market expansion to capitalize on its strengths and overcome its weaknesses.


















Leave a Comment