Market Trends
Key Emerging Trends in the India Electric Car Market
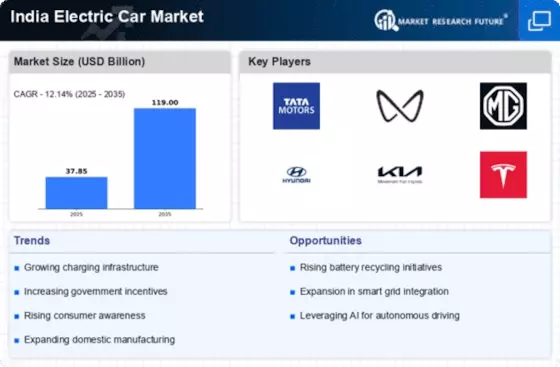
In recent years, the Indian electric car market has witnessed a notable surge in activity, reflecting both global trends towards sustainable transportation and India's own push for cleaner energy solutions. One prominent trend is the increasing consumer interest in electric vehicles (EVs) due to growing environmental awareness and concerns over air pollution. This shift in consumer preferences has been bolstered by government initiatives aimed at promoting EV adoption, such as subsidies, tax incentives, and infrastructure development. As a result, major automakers have begun to introduce a variety of electric car models tailored to the Indian market, offering consumers more choices and driving competition within the industry.
Moreover, technological advancements and decreasing battery costs have played a crucial role in driving the market trends of electric cars in India. With improvements in battery technology, EVs are becoming more affordable and capable of longer ranges, addressing two major concerns among potential buyers—cost and range anxiety. This has led to increased confidence in electric vehicles as viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Additionally, the availability of charging infrastructure has expanded rapidly across major cities in India, further bolstering consumer confidence in the practicality of electric cars for everyday use.
Another significant trend in the Indian electric car market is the rise of electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers. These smaller electric vehicles have gained popularity due to their affordability, efficiency, and suitability for urban commuting. With congested city streets and rising fuel prices, electric scooters and rickshaws offer a compelling alternative for short-distance travel, contributing to the overall electrification of the transportation sector in India.
Furthermore, the government's ambitious targets for electric mobility have provided a strong policy framework to drive market growth. Initiatives such as the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme aim to accelerate the adoption of EVs by providing subsidies and incentives for both consumers and manufacturers. Additionally, regulatory measures such as stricter emissions standards and mandates for electrifying public transportation fleets are further incentivizing the transition towards electric mobility.
Collaborations and partnerships between domestic and international players have also become prevalent in the Indian electric car market. Indian automakers are forming alliances with global EV manufacturers to leverage their expertise in electric vehicle technology and accelerate product development. These partnerships not only facilitate technology transfer but also enhance market penetration through established distribution networks and brand recognition.
Despite these positive developments, challenges remain in scaling up the electric car market in India. High upfront costs, limited charging infrastructure in rural areas, and concerns over battery recycling and disposal present significant hurdles to widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges will require continued investment in research and development, infrastructure deployment, and public awareness campaigns.
In conclusion, the Indian electric car market is witnessing dynamic growth driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, supportive government policies, and industry collaborations. While significant progress has been made, concerted efforts are needed to overcome remaining barriers and realize the full potential of electric mobility in India. With continued innovation and investment, electric vehicles are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation in the country.
















Leave a Comment