Market Trends
Introduction
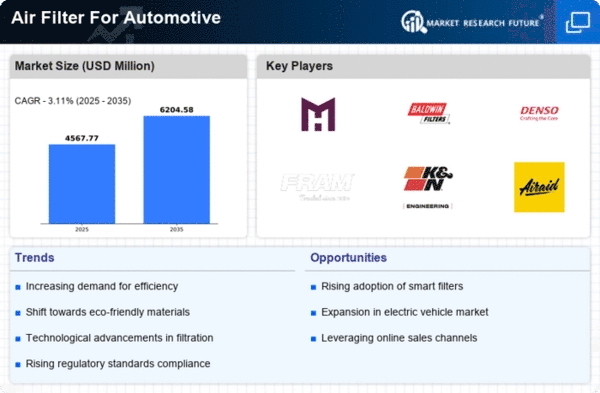
A SERIES OF MACRO FACTORS WILL DRIVE THE MARKET FOR AIR FILTERS INTO A CERTAIN DIRECTION. A new generation of filtration materials and designs are improving performance and efficiency. Regulatory requirements to reduce vehicle emissions are pushing manufacturers to adopt innovations. And the shift in consumer behavior towards greater concern for health and the environment is driving demand for high-quality filtration solutions. These macro trends are of strategic importance for industry players. They not only influence product development and market positioning, but also compliance strategies and customer engagement approaches in an increasingly competitive environment.
Top Trends
-
Increased Focus on Cabin Air Quality
In recent years, car manufacturers have paid particular attention to the air quality in the passenger compartment. Regulations, for example, requiring higher filtration standards in Europe, have prompted innovation. The use of HEPA filters, which remove up to 99.99% of airborne particles, is now commonplace. This trend is likely to drive R&D into the development of more advanced filtration systems. -
Integration of Smart Technologies
In the meantime, the Internet of Things and smart technology are being incorporated into filters, enabling the real-time monitoring of filter performance. Companies like Denso are developing smart filters that warn when they need replacing. This innovation will reduce maintenance costs and improve vehicle performance, establishing a new standard for future automobiles. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
The market for automobile air filters is becoming a field where biodegradable and recyclable materials are being researched. Mahle, for example, has launched filters made from sustainable resources, in line with the goals of the world climate convention. The change not only meets the demand for greener products, but also gives companies a competitive advantage. -
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Vehicle manufacturers are being forced to improve the filtration systems for exhaust gases, because stricter regulations are being enforced all over the world. The example of the European Union’s introduction of the EURO 7 standard is a good example. The stricter the regulation, the higher the costs of compliance and the market access, the higher the investment in advanced filtration systems. -
Growth of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The electric car is reshaping the air-cleaning market. The filtration of the air in electric cars requires a different filtration system than in conventional cars. These filters are being developed by companies such as Bosch. They focus on efficiency and performance. This development is expected to increase the market for new filtration systems in the electric car segment. -
Enhanced Filtration Efficiency
There is a growing demand for high-efficiency filters that are able to filter out smaller particles. This is due to a growing awareness of the health effects of particulate matter. Research has shown that filters with a MERV 13 rating or higher can significantly improve the air quality. The trend is driving manufacturers to invest in new materials and technology to keep up with the competition. -
Aftermarket Filter Solutions
The market for replacement car air filters is growing as consumers seek cost-effective alternatives. Mann+Hummel has responded to this trend with high-quality replacement filters. This is an important market for the company because it maintains vehicle performance and offers a good revenue opportunity for manufacturers. -
Collaboration and Partnerships
A growing number of strategic alliances between the automobile industry and the filtration industry are being established in order to develop new products. The Freudenberg Group, for example, is working with the car manufacturers to develop the next generation of filtration systems. Such strategic alliances can accelerate the development of products and thus improve their competitiveness in the market. -
Digitalization in Manufacturing Processes
The introduction of digital technology into the manufacturing process has completely transformed the production of air filters. The use of automation and data analysis has made it possible to optimize the production process and reduce waste. This will reduce operating costs and improve product quality. -
Consumer Education and Awareness
The consumers' knowledge of the importance of air quality has led to a growing demand for manufacturers to launch educational initiatives. The benefits of high-quality filters are being promoted in marketing campaigns. This is likely to influence the consumers' buying behavior and to drive the sales of premium filters.
Conclusion: Navigating the Competitive Air Filter Landscape
The car air filter market in 2024 is characterized by a very intense competition and significant fragmentation, with a large number of both established and new players. The focus on environment and compliance with regulations has led to innovation in the products offered by the suppliers. The established companies can count on established brand loyalty and a distribution network, while the new ones can count on a more advanced ability such as artificial intelligence-driven filtration and automation of the production process. Those who wish to be in a leading position in the market must be able to integrate the environment and be flexible in product development. The management must therefore allocate resources to these capabilities in order to be able to navigate the complex market and take advantage of the emerging opportunities.


















Leave a Comment