Emerging Treatment Options
The Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market is poised for growth due to the emergence of novel treatment options. Recent developments in pharmacological therapies, such as anti-VEGF agents and complement inhibitors, show promise in managing dry AMD. These innovative treatments may improve visual outcomes and slow disease progression, thereby attracting more patients to seek care. Additionally, clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of these new therapies, which could further enhance the treatment landscape. As these options become available, they are likely to drive demand within the Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market, offering hope to patients and healthcare providers alike.
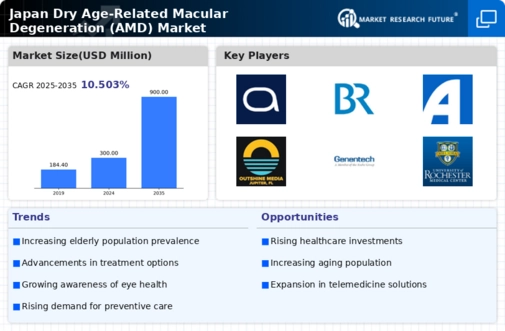
Rising Aging Population in Japan
The Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market is significantly influenced by the increasing aging population. As of 2025, approximately 28% of Japan's population is aged 65 and older, a demographic that is particularly susceptible to dry AMD. This trend is expected to continue, leading to a higher incidence of age-related eye diseases. The growing number of elderly individuals necessitates enhanced healthcare services and treatment options, thereby driving demand within the market. Furthermore, the Japanese government has recognized this demographic shift and is likely to implement policies aimed at improving eye health services. This focus on geriatric care may lead to increased funding for research and development in the Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Increased Awareness and Education
Awareness regarding dry AMD is gradually increasing among the Japanese population, which is positively impacting the Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market. Educational campaigns by healthcare organizations and non-profits are informing the public about the symptoms and risks associated with dry AMD. This heightened awareness encourages individuals to seek early diagnosis and treatment, which is crucial for managing the disease effectively. As more people become informed about the importance of regular eye examinations, the demand for screening and therapeutic options is likely to rise. Consequently, this trend may lead to a more proactive approach to eye health, further stimulating growth in the Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market.
Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies
The Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market is experiencing growth due to advancements in diagnostic technologies. Innovations such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus photography have improved the accuracy of dry AMD diagnosis. These technologies enable healthcare professionals to detect the disease at earlier stages, which is essential for effective management. As diagnostic tools become more accessible and affordable, healthcare providers are likely to adopt them more widely, leading to increased patient referrals for treatment. This shift not only enhances patient outcomes but also contributes to the overall expansion of the Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market, as more individuals are diagnosed and treated.
Government Support and Policy Initiatives
The Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market benefits from government support and policy initiatives aimed at improving eye health. The Japanese government has implemented various programs to promote research and development in ophthalmology, particularly focusing on age-related diseases. These initiatives may include funding for clinical trials and partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to expedite the development of new treatments. Furthermore, public health campaigns aimed at educating the population about eye health are likely to enhance early detection and treatment of dry AMD. This supportive environment fosters innovation and growth within the Japan Dry Age Related Macular Degeneration Amd Market, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers.