Supportive Regulatory Frameworks
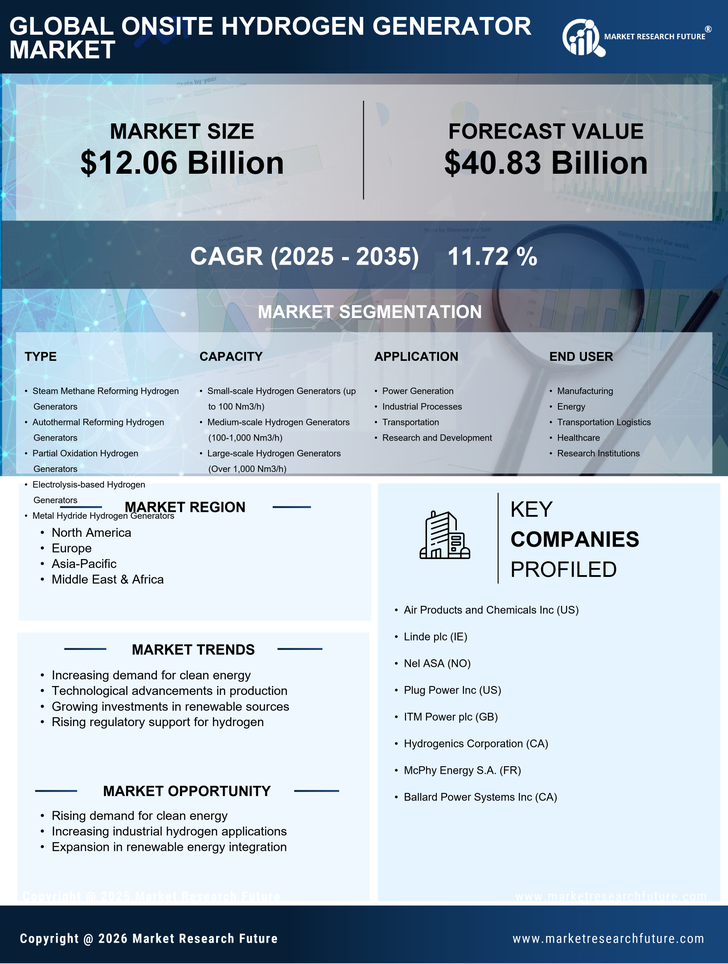
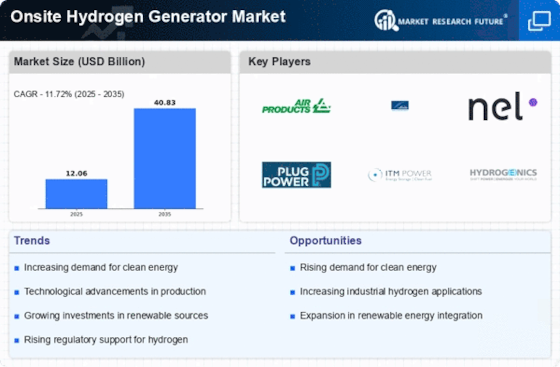
The Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market benefits from supportive regulatory frameworks that encourage the adoption of hydrogen technologies. Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives aimed at promoting clean energy solutions, including hydrogen production. These regulations often include tax credits, grants, and subsidies for companies investing in hydrogen infrastructure. For instance, several countries have set ambitious targets for hydrogen adoption as part of their climate action plans. This regulatory support not only fosters a conducive environment for the growth of the Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market but also instills confidence among investors and stakeholders, further propelling market expansion.
Rising Demand for Clean Energy Solutions
The Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market is experiencing a notable surge in demand for clean energy solutions. As industries and governments increasingly prioritize sustainability, hydrogen emerges as a viable alternative to fossil fuels. The transition towards hydrogen is driven by its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly. According to recent estimates, the hydrogen market is projected to reach a value of approximately 200 billion USD by 2030, indicating a robust growth trajectory. This shift is not merely a trend but a fundamental change in energy consumption patterns, as sectors such as transportation, manufacturing, and power generation seek to adopt cleaner technologies. Consequently, the Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market stands to benefit from this growing inclination towards environmentally friendly energy sources.
Growing Applications Across Various Industries
The Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market is expanding due to the growing applications of hydrogen across various sectors. Industries such as transportation, chemical manufacturing, and energy storage are increasingly recognizing the versatility of hydrogen as a clean energy carrier. For example, hydrogen fuel cells are gaining traction in the automotive sector, while chemical industries utilize hydrogen for processes like ammonia production. This diversification of applications is likely to drive demand for onsite hydrogen generation solutions, as companies seek to integrate hydrogen into their operations. As a result, the Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market is poised for substantial growth, reflecting the broader trend of hydrogen adoption across multiple sectors.
Cost-Effectiveness of Onsite Hydrogen Production
The Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market is increasingly recognized for its cost-effectiveness in hydrogen production. By generating hydrogen on-site, companies can significantly reduce transportation and storage costs associated with traditional hydrogen supply chains. This localized production model not only minimizes logistical expenses but also enhances supply chain reliability. Recent analyses suggest that onsite hydrogen generation can lower costs by up to 30% compared to conventional methods. As industries seek to optimize operational efficiency and reduce overheads, the appeal of onsite hydrogen generation becomes more pronounced. This economic advantage positions the Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market favorably, particularly in sectors where hydrogen is a critical input.
Technological Innovations in Hydrogen Generation
The Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market is witnessing rapid technological innovations that enhance the efficiency and reliability of hydrogen production. Advances in electrolysis technology, for instance, have led to the development of more efficient systems capable of producing hydrogen at lower energy costs. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into hydrogen generation processes is becoming increasingly feasible. These innovations not only improve the overall efficiency of hydrogen production but also align with sustainability goals. As a result, the Onsite Hydrogen Generator Market is likely to see increased adoption of these advanced technologies, driving further growth and investment.