Market Trends
Introduction
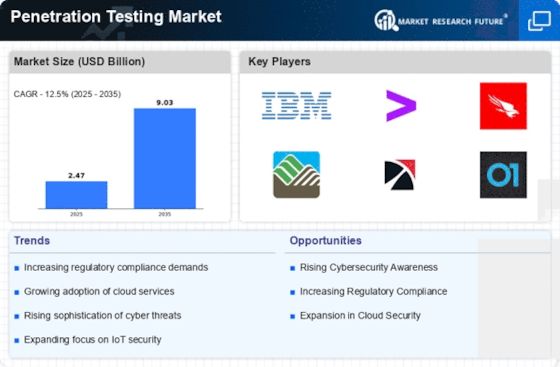
During the period 2023–2024 the penetration testing market is experiencing a great deal of change, owing to a confluence of macroeconomic factors. The emergence of the cloud and the rapid proliferation of IoT devices are reshaping the threat landscape and making more sophisticated security measures necessary. In addition, the regulatory burden is becoming more onerous, with organizations subject to stricter compliance regulations that require regular penetration testing. Furthermore, changes in consumer behavior, with a growing awareness of cyber threats, are compelling businesses to prioritise robust security frameworks. These macroeconomic trends are of strategic importance to the penetration testing market, highlighting the need for a flexible approach to security and the development of new solutions that can cope with emerging threats and ensure compliance in an increasingly complex digital environment.
Top Trends
-
Increased Regulatory Compliance
Governments are imposing stricter cyber regulations, and penetration testing is being embraced by organizations as a means of achieving compliance. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the United States’ CMMI require companies to perform regular security audits. A recent survey revealed that 70% of organizations are prioritizing compliance-related security measures. This trend will lead to increased penetration testing as organizations seek to avoid fines and reputational damage. -
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have greatly improved the detection of threats. Artificial intelligence has facilitated the automation of vulnerability testing at companies like Rapid7, resulting in a reduction of vulnerability testing time by as much as 30 percent. This trend will continue and will lead to more sophisticated tools that will simulate attacks in real time and allow for more proactive security measures. -
Shift Towards Continuous Testing
In order to keep up with the ever-changing threat landscape, organizations are moving from periodic penetration testing to continuous testing. A recent survey showed that more than half of organizations are already adopting continuous testing. This shift is driven by the need for real-time visibility into security posture, which leads to more agile security operations and quicker remediation of vulnerabilities. -
Cloud Security Focus
In the cloud, as companies increasingly migrate to the cloud, penetration testing is concentrating on the cloud’s weaknesses. A study shows that 80% of companies have had security incidents in the cloud in the past year. The penetration testing of cloud computing is now being developed by the service provider. -
Emphasis on IoT Security
With the growing proliferation of IoT devices, penetration testing is extending to IoT security assessment. By the year 2030, according to some studies, the number of IoT devices will have reached 50 billion. The need to protect the enterprise from the risks of connected devices is leading to the development of new testing methodologies. -
Collaboration with Ethical Hackers
A growing number of organizations are working with ethical hackers to improve their security posture. HackerOne, for example, has seen a 40 percent increase in bug bounty programs. This trend is fostering a culture of security awareness and innovation, as companies realize the value of diverse perspectives in identifying and addressing security issues. -
Focus on Application Security
As the speed of development of applications increases, there is a growing focus on security through penetration testing. A survey* found that 75% of organizations consider application security to be their top priority in their testing strategies. This trend is driving the demand for specialized penetration testing services, which help to identify and remediate application security risks before deploying the application. -
Remote Work Security Challenges
This has prompted organizations to review their penetration testing strategy. A recent survey indicated that a whopping 90 per cent of IT managers are worried about the security of their remote workers. This trend has increased demand for remote penetration testing services as companies seek to secure their remote workers from the threat of cyber attacks. -
Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
There is a growing need for a better reporting and analytics in penetration testing. Companies want more details, more insights and more actionable recommendations from the penetration test reports. A survey has found that 65% of the companies value detailed reports to make decisions. This trend is driving the penetration testing service providers to invent new reporting tools and methods that improve the overall effectiveness of penetration testing. -
Cybersecurity Skills Gap
A lack of security skills is affecting the penetration testing market, with a shortage of qualified personnel. A survey has found that seventy per cent of companies have difficulties finding penetration testing specialists. This is resulting in an increased investment in training and automation, as companies seek to close the skills gap and improve their security capabilities.
Conclusion: Navigating the Competitive Landscape Ahead
As we look to 2024, penetration testing is characterized by intense competition and significant fragmentation, with the leading and emerging players vying for market share. And in North America and Europe, the trend is towards a greater need for bespoke solutions. Consequently, penetration testing vendors must strategically position themselves by deploying advanced capabilities such as artificial intelligence and automation to enhance service delivery and efficiency. The need for flexibility and adaptability to meet changing client needs and regulatory requirements is also becoming a key differentiator. To keep pace with this fast-changing environment, penetration testing vendors must also focus on strategic alliances and innovation.















Leave a Comment