Market Trends
Introduction
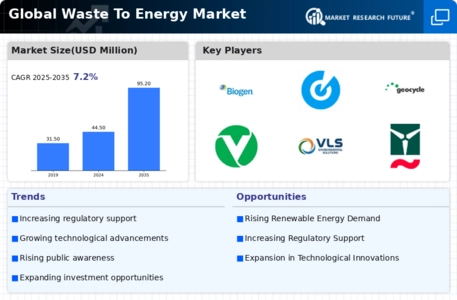
Waste to Energy (WtE) is experiencing a major transformation as it heads towards 2025, driven by a confluence of macro-economic factors. In particular, technological advancements are improving the efficiency and viability of WtE processes, while regulations are increasingly requiring waste management practices to be sustainable, and thus putting pressure on all parties to adapt. In addition, changes in the consumer’s attitudes towards sustainable practices are influencing the demand for cleaner energy solutions, which is further driving the WtE market. These trends are strategically important for all parties involved, as they not only support the international goals for sustainable development, but also present opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage in the energy landscape.
Top Trends
-
Increased Adoption of Advanced Technologies
Waste to energy is experiencing a surge in advanced technologies like gasification and pyrolysis. In the UK, the most advanced are companies like Bluefire, with its gasification plants converting waste into syngas. Some plants are already claiming a waste-to-energy efficiency of up to 90 per cent. As the technology develops, it is expected that operating costs will fall, making the technology more affordable for local authorities. -
Government Incentives and Regulations
Governments all over the world are making waste disposal increasingly difficult, which is driving the development of waste-to-energy solutions. In Europe, for example, the European Union has set ambitious recycling targets, which in turn is encouraging companies such as Veolia to invest. Regulations such as these will create a more favourable business environment, encourage public-private collaboration, and increase the number of waste-to-energy plants in use in cities. -
Focus on Circular Economy Principles
The concept of the circular economy is becoming more and more important, with Waste to Energy playing a crucial role in resource recovery. Waste management and energy production are a single entity for GEOCYCLE. This trend is supported by the growing demand for sustainable practices from consumers, and has resulted in an increase in investment in waste-to-energy projects that contribute to the circular economy. -
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Waste-to-Energy plants are increasingly being combined with other forms of energy from natural sources. For example, AXPO Holding AG is exploring the possibility of hybrid systems combining solar energy with Waste-to-Energy. The combination not only diversifies the energy sources, but also ensures greater stability in the grid. This is an important step in the process of meeting the goals set for renewable energies. -
Emergence of Decentralized Energy Systems
Waste to energy systems are gaining in popularity, especially in remote and under-developed areas. In recent years, smaller, locally deployable systems have been developed by companies such as BTA International GMBH. These systems have the potential to reduce transport costs, increase the security of energy supply and to change the energy landscape in the long term. -
Enhanced Public Awareness and Engagement
Awareness of the importance of waste management and energy recovery is growing, and this awareness is influencing policy and investment decisions. In the process, organisations such as Viridor are educating the public about the benefits of waste-to-energy. This growing public awareness will lead to a greater demand for local projects, and more community-based initiatives and funding opportunities. -
Collaboration Across Industries
Waste to Energy (WtE) technology requires interdisciplinary collaborations to be successful. In Ramboll’s case, this means bringing together waste management companies and energy companies. This is expected to facilitate the development of integrated solutions and ultimately benefit the entire waste management system. -
Investment in Research and Development
Research and development of waste-to-energy technology is on the increase, driven by the need for more efficient processes. Companies like Emery Energy are developing new ways to extract energy from waste. This is likely to lead to a step change in energy output and reduction in emissions, and put companies at the forefront of the industry. -
Focus on Carbon Neutrality Goals
With the world's focus on carbon neutrality, waste to energy is a viable solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Strategic companies like Babcock & Wilcox are aligning their business with climate goals, promoting waste to energy as a cleaner alternative. This focus is expected to attract investment and drive innovation, and position the industry as a key player in the transition to a low-carbon economy. -
Utilization of Waste Heat Recovery
Waste heat recovery is becoming a critical component of waste to energy systems, increasing their overall efficiency. Companies are increasingly investing in heat recovery from energy production. This trend is expected to increase the energy efficiency of the industry by up to 30 percent. This will make the industry more sustainable and profitable and will also reduce the carbon footprint of the energy produced.
Conclusion: Navigating the Waste To Energy Landscape
Towards 2025, the waste-to-energy market is characterised by a high level of competition and considerable fragmentation, with both established and new entrants competing for market share. Regional trends are increasingly focusing on sustainability and regulatory compliance, which is forcing suppliers to adapt their strategies accordingly. The leading players are making use of their established infrastructures, and are integrating new capabilities, such as artificial intelligence and automation, to increase their operational efficiency. While newcomers are focusing on flexibility and disruptive technology to disrupt the established order. The ability to use artificial intelligence for predictive analysis, to automate processes and to focus on sustainability will be critical to market leadership. These capabilities will have to be prioritised by decision-makers to keep up with the changing landscape and seize emerging opportunities.









Leave a Comment