Fuel Cells for Marine Vessels Market
Introduction
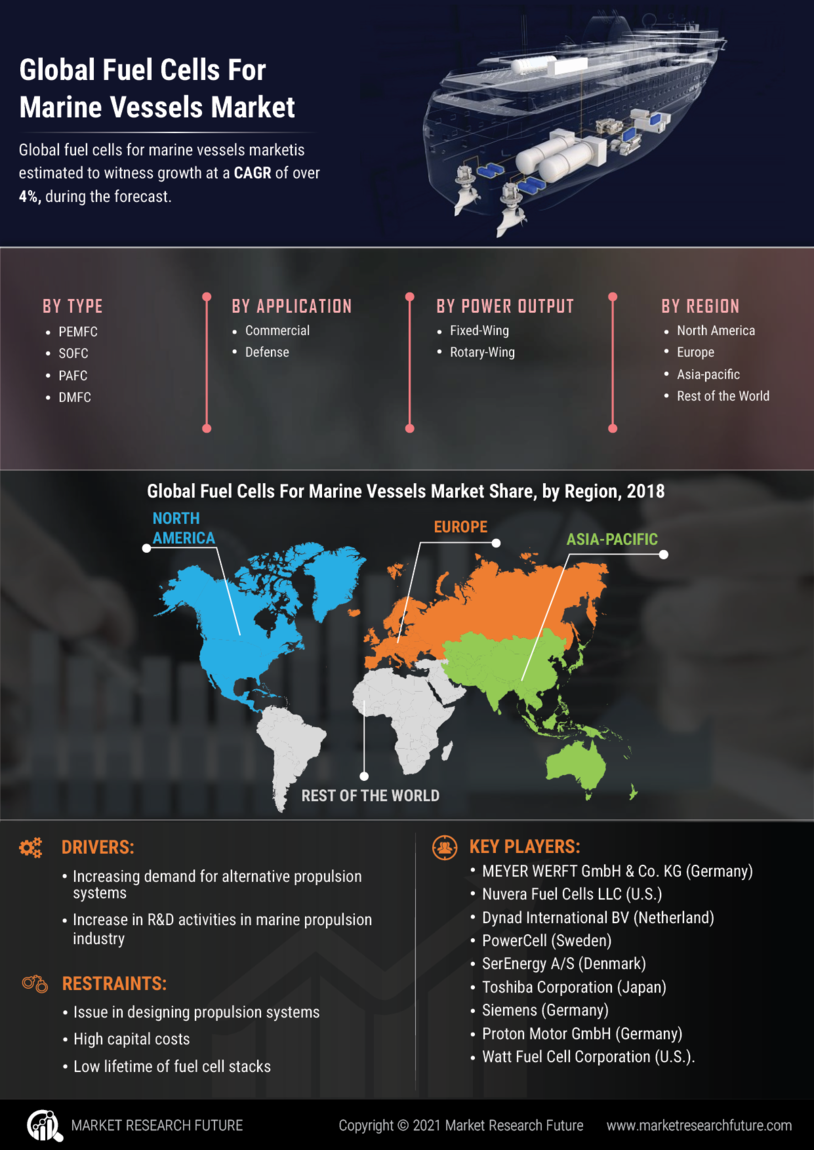
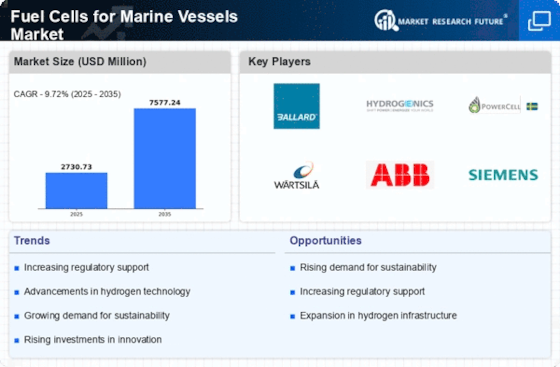
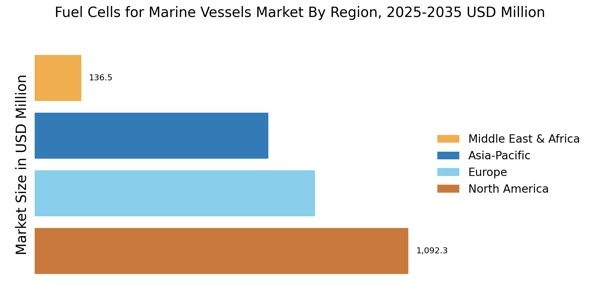
In recent years, the marine transportation sector has witnessed a significant increase in demand for energy-efficient alternatives and pollution control mechanisms amid increasing environmental scrutiny. The global fuel cells for marine vessels market is, therefore, expected to be driven by the surging demand for fuel cells as an alternative source of energy for marine vessel applications. This research report provides a comprehensive understanding of the global fuel cells for marine vessels market from the demand and supply perspectives, covering market growth indicators, key drivers, restraining factors, and emerging opportunities.
Research Methodology
The research methodology applied to this report focuses on conducting an in-depth and extensive assessment of the global fuel cells marine vessels market from a demand-side as well as a supply-side perspective. The research approach involves secondary data mining, primary data collection and evaluation, and data validation through triangulation to analyze the collected information in a detailed manner.
Market Definition
The fuel cells marine vessels market is defined as the segment of fuel cell technology applied to the marine transportation sector. Essentially, fuel cells are electrochemical cells that convert a combination of hydrogen and oxygen into electricity while leaving water as a by-product. Fuel cell technology is based upon the principle of chemical energy conversion and is considered a more efficient and clean energy source than traditional thermo-chemical combustion technologies. It is expected to experience an accelerated adoption of fuel cell-powered marine vessels in the subsequent years due to the growing demand for cleaner, more sustainable energy sources.
Secondary Data Collection
Secondary research forms the base of the research methodology adopted for this report. The process entailed data mining through extensive databases and sources such as annual reports, general publications, corporate publications, white papers, industry associations, market reports, and others. The research process involved several aspects, such as tracking existing and emerging industry and technological trends, studying the macro and micro economic factors governing the industry, tracking the initiative of market players, regulatory mapping and market-entry dynamics among others.
Primary Data Collection
Primary research is constituted of primary data collection and validation done through in-person or telephonic interviews with industry experts and market participants. For the sake of the research, experts in the industry, such as suppliers, distributors, manufacturers, and end-use sectors were approached. The collected information was then verified and validated through both qualitative and quantitative data triangulation.
Data Analysis
The collected data is further analyzed using multiple tools, such as factor analysis, time-series analysis, supporting document review and industry mapping. The research methodology also included data interpretation involving percentage share and market attractiveness index. The different approaches used to analyze the data and arrive at suitable conclusions were the top-down approach, the bottom-up approach and demand and supply side data triangulation.
Conclusion
The research methodology entailed collecting both primary data as well as secondary information to conduct an in-depth and comprehensive assessment of the global fuel cells marine vessels market from a demand-side as well as a supply-side perspective. Key market growth indicators, drivers, restraints and key emerging opportunities in the market were identified through the research. Factors such as factor analysis, time-series analysis, top-down approach, bottom-up approach and demand and supply side data triangulation were applied to analyze the collected data and arrive at suitable conclusions.