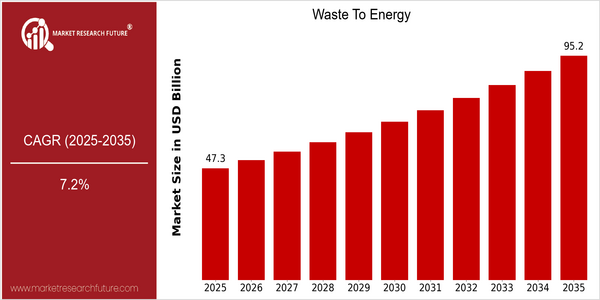
Waste To Energy Size
Market Size Snapshot
| Year | Value |
|---|---|
| 2025 | USD 47.34 Billion |
| 2035 | USD 95.19 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 7.2 % |
Note – Market size depicts the revenue generated over the financial year
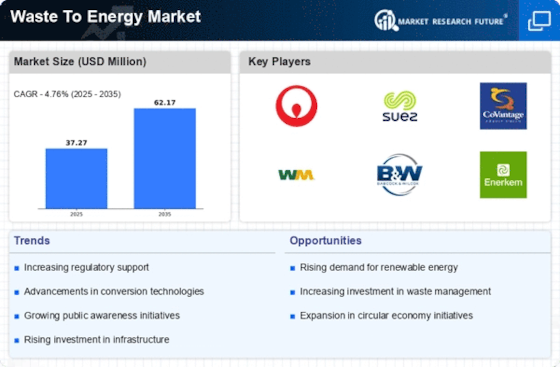
The waste-to-energy market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2035. The trend towards growth is based on the growing emphasis on sustainable waste management and the transition to circular economies. As urbanization accelerates and waste production increases, there is a growing demand for waste-to-energy systems that can convert waste into energy. The growth is based on several factors, such as the development of new waste treatment and conversion technology, increased government regulations promoting the use of renewable energy, and a growing public awareness of the need to manage waste sustainably. Anaerobic digestion, gasification, and other innovations are improving the efficiency and commercial viability of waste-to-energy systems. The major players, such as Veolia, Covanta, and Suez, are investing in new technology and forming strategic alliances to strengthen their market positions. Recent alliances aimed at developing integrated waste management systems demonstrate the industry’s commitment to using technology to produce sustainable energy.
Regional Market Size
Regional Deep Dive
Waste-to-Energy (WtE) market is experiencing a considerable growth in various regions, due to the increasing amount of waste and the stringent regulations and the increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions. Each region has its own characteristics, which are influenced by the local policy, economic situation and cultural attitudes to waste management and sustainable energy. A common thread is the transition to a circular economy, where many regions are investing in new technology to convert waste into energy and thereby reduce the use of land filling and greenhouse gas emissions.
Europe
- Waste to Energy (WtE) is a comparatively new process in the world, but is already well established in many countries of the European Union.
- Amongst the companies that are preparing for the future are Veolia and Suez. They are investing in the most advanced projects of waste-to-energy, which not only produce energy but also produce a valuable by-product, such as biofertilizer, thereby enhancing the overall performance of waste management.
Asia Pacific
- Japan and South Korea are the pioneers of the WtE industry. They are driven by a lack of space for disposal and by a strong government policy promoting energy self-sufficiency. Japan’s Public Health and Municipal Waste Management Law, for example, facilitates the establishment of WtE plants.
- In India, for example, where the public-private partnership has become commonplace, companies like GMR and Ramky Enviro Engineers are making huge investments in waste-to-energy projects. Such projects address two major concerns: the management of solid waste and the generation of energy.
Latin America
- Brazil is emerging as a leader in the WtE sector in Latin America, with the government promoting WtE projects through the National Solid Waste Policy, which encourages the use of waste as a resource for energy generation.
- The Green Energy Initiative in So Paulo shows the possibilities of converting organic waste into biogas, in partnership between local and international companies.
North America
- The EPA has pushed for WtE technology through several initiatives, including the Waste Management Hierarchy, which puts a priority on waste reduction and energy recovery and encourages the construction of WtE plants.
- In many states, for example California and New York, ambitious goals for the use of renewable energy sources have been set. Waste-to-energy plays an important role in this. The number of new projects has therefore increased and there is a lot of interest in the construction of WtE facilities.
Middle East And Africa
- The Waste Management Strategy for the United Arab Emirates for the Year 2021 has been launched with the objective of reducing the rate of waste disposal to 75% and to promote the WtE process as a viable alternative. Projects like the Waste to Energy Plant in Dubai are expected to make a significant contribution to the energy mix in the region.
- In South Africa, the government is investigating WtE as part of its Integrated Resources Plan. It is developing a number of pilot projects to convert waste into energy, with the support of the South African National Energy Development Institute.
Did You Know?
“Did you know that the WtE process can reduce the volume of waste by up to 90%, significantly decreasing the need for landfill space?” — EPA, 2023
Segmental Market Size
Waste-to-energy plays a vital role in the overall waste management chain and is currently a fast-growing market, driven by rising waste volumes and the need for sustainable energy solutions. The key drivers of growth are the increasingly stringent regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing waste sent to landfill and increasing the amount of energy recovered from waste, as well as technological developments in the field of waste treatment. In Europe and North America, waste-to-energy operators such as Veolia and Covanta are already operating large-scale municipal solid waste-to-energy plants. Waste-to-energy is used mainly to produce electricity, district heating and biofuels. Recent examples of successful implementation include the Amsterdam Waste-to-Energy Plant and the Copenhagen Waste-to-Energy Plant. A growing number of countries are now focusing on a more sustainable approach to waste management and are aiming to meet government targets for the share of energy from renewable sources. The future of waste-to-energy is dependent on the development of anaerobic digestion and gasification technology, which enables the treatment of waste in a more efficient way and reduces the impact on the environment.
Future Outlook
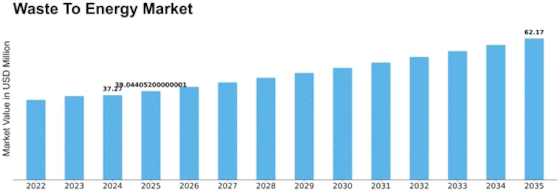
The waste to energy (WtE) market is expected to experience a significant growth between 2025 and 2035, growing from USD 47.34 billion to USD 95.191 billion. This represents a high compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. This growth is attributed to the rising waste generation, which is expected to reach 3.4 billion tons by 2030, and the increasing demand for sustainable waste management solutions. In the long run, as urbanization accelerates and regulations become more stringent, the use of WtE will become more important to meet the waste disposal challenges while generating clean energy. By 2035, it is expected that WtE facilities will convert approximately 15% of the municipal solid waste (MSW) generated worldwide, a significant increase from the current level. The key technological drivers, such as advancements in gasification and anaerobic digestion, will further improve the efficiency and output of WtE plants, making them more attractive to investors and local governments. Also, the integration of digital technology, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), will optimize the operations and improve the waste sorting process, which will further increase the recovery rates. The circular economy, and the incentive schemes for the production of green energy will also be a major growth driver. The increasing awareness of the dual benefits of waste management and energy production will also lead to the WtE industry playing a key role in the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.


















Leave a Comment