Rising Demand for Electronics
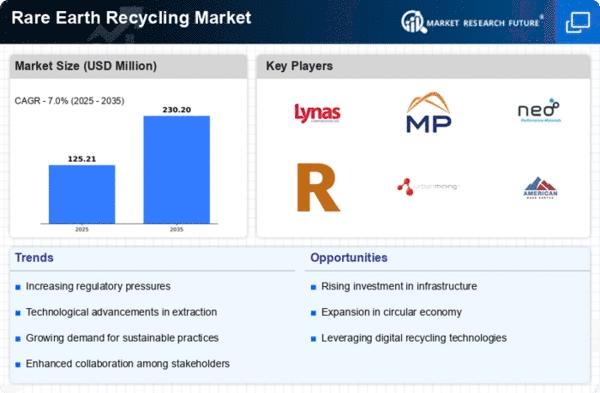
The Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry experiences heightened demand due to the proliferation of electronic devices. As consumers increasingly rely on smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, the need for rare earth elements, such as neodymium and dysprosium, escalates. This trend is projected to drive the market's value to approximately 631.9 USD Million in 2024. The recycling of these materials not only addresses supply chain vulnerabilities but also mitigates environmental concerns associated with mining. Thus, the Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry is poised for growth as manufacturers seek sustainable sourcing solutions.
Global Supply Chain Challenges
The Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry is significantly influenced by ongoing supply chain challenges related to rare earth materials. Geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions have highlighted the vulnerabilities of relying on primary sources for these critical materials. As a result, companies are increasingly turning to recycling as a viable alternative to secure their supply chains. This trend is expected to drive the market's growth, as organizations seek to mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions. The focus on recycling rare earth elements is likely to become a strategic priority for many industries, further solidifying the market's importance in the global economy.
Government Regulations and Initiatives
Governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations to promote recycling and reduce environmental impact, significantly influencing the Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry. Policies aimed at minimizing waste and encouraging the recovery of rare earth elements from discarded products are becoming more prevalent. For instance, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan emphasizes recycling and resource efficiency, which could enhance the market's growth trajectory. As these regulations take effect, the market is expected to expand, potentially reaching 974.8 USD Million by 2035, as companies adapt to comply with new standards and capitalize on recycling opportunities.
Technological Advancements in Recycling Processes
Innovations in recycling technologies are transforming the Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry. Advanced techniques, such as hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes, are improving the efficiency of rare earth recovery from electronic waste. These technological advancements not only enhance recovery rates but also reduce operational costs, making recycling more economically viable. As a result, the market is likely to witness a compound annual growth rate of 4.02% from 2025 to 2035. This growth is indicative of the industry's potential to meet the rising demand for rare earth elements while promoting sustainable practices.
Increasing Awareness of Environmental Sustainability
There is a growing awareness of environmental sustainability among consumers and industries, which is positively impacting the Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry. As stakeholders recognize the ecological consequences of rare earth mining, the push for recycling becomes more pronounced. Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, driven by consumer demand for eco-friendly products. This shift is likely to bolster the market's growth, as businesses seek to enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles. The emphasis on sustainability is expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future landscape of the Global Rare Earth Recycling Market Industry.