US Clinical Trials Market Summary
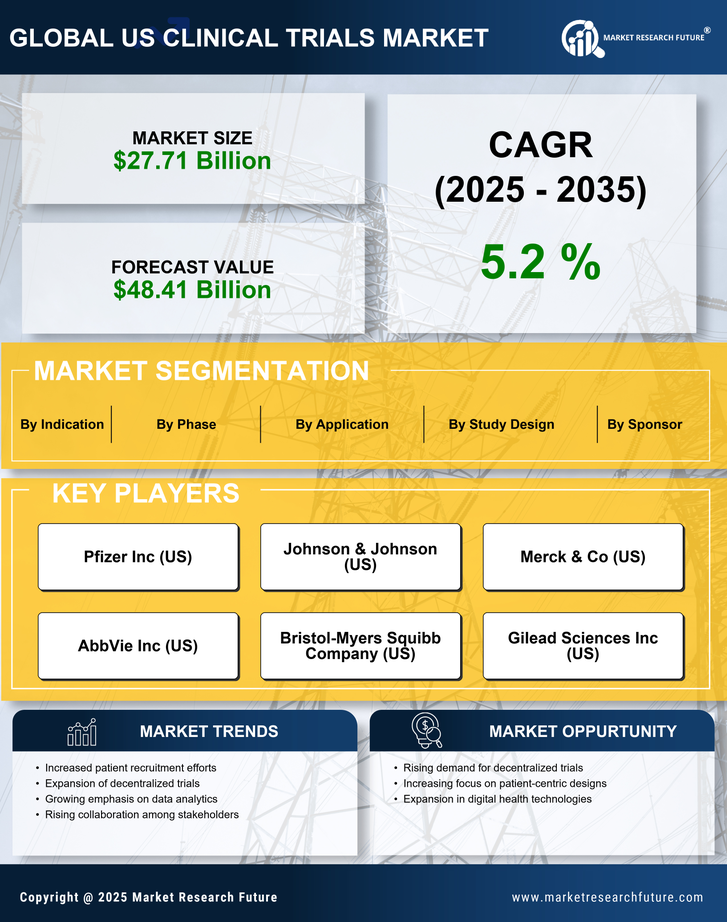
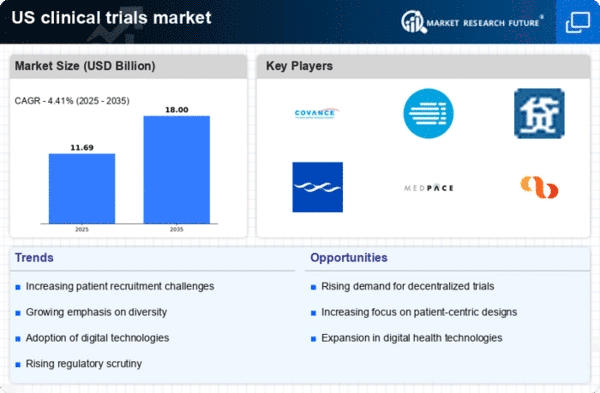
As per Market Research Future analysis, the US clinical trials market size was estimated at 11.2 USD Billion in 2024. The US clinical trials market is projected to grow from 11.69 USD Billion in 2025 to 18.0 USD Billion by 2035, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% during the forecast period 2025 - 2035
Key Market Trends & Highlights
The US clinical trials market is experiencing a transformative shift towards digitalization and patient-centric methodologies.
- The market is witnessing an increased use of digital technologies to enhance trial efficiency and data collection.
- There is a growing emphasis on patient-centric approaches, which prioritize participant engagement and experience.
- Regulatory adaptations are facilitating faster approvals, thereby accelerating the clinical trial process.
- Key market drivers include the rising demand for innovative therapies and advancements in biopharmaceuticals.
Market Size & Forecast
| 2024 Market Size | 11.2 (USD Billion) |
| 2035 Market Size | 18.0 (USD Billion) |
| CAGR (2025 - 2035) | 4.41% |
Major Players
Covance (US), IQVIA (US), PPD (US), Charles River Laboratories (US), Medpace (US), Syneos Health (US), Parexel International (US), Wuxi AppTec (CN), KCR (PL)