Market Growth Projections
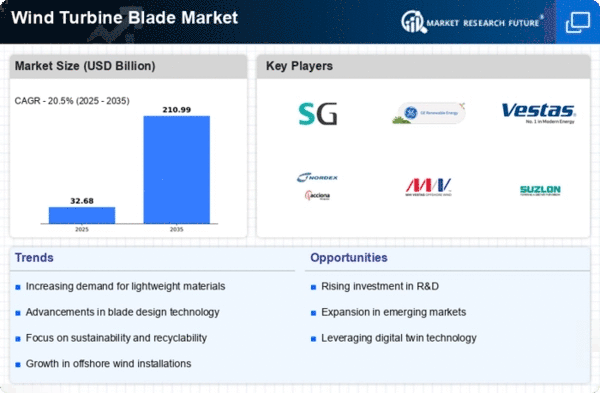
The Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry is projected to experience substantial growth, with estimates indicating a market value of 27.1 USD Billion in 2024 and a remarkable increase to 211.0 USD Billion by 2035. This growth trajectory reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.5% from 2025 to 2035. Such projections underscore the increasing investments in wind energy infrastructure and the ongoing advancements in turbine technology. The market's expansion is likely to be driven by a combination of factors, including rising energy demands, government support, and technological innovations.
Government Incentives and Support
Government incentives play a crucial role in propelling the Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry. Many nations offer subsidies, tax credits, and grants to promote wind energy projects, making them more financially viable. For example, the United States has implemented the Production Tax Credit, which has significantly boosted investments in wind energy. Such supportive policies not only encourage the development of new wind farms but also stimulate the demand for turbine blades. As the market expands, it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20.5% from 2025 to 2035, reflecting the positive impact of government initiatives on the industry.
Rising Demand for Renewable Energy
The Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry experiences a surge in demand for renewable energy sources, driven by global initiatives to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Governments worldwide are implementing policies that favor the adoption of wind energy, resulting in increased investments in wind power projects. For instance, the global wind energy capacity is projected to reach 1,200 GW by 2024, significantly contributing to the anticipated market value of 27.1 USD Billion. This trend indicates a robust growth trajectory for the Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry as more countries commit to sustainable energy solutions.
Increasing Energy Security Concerns
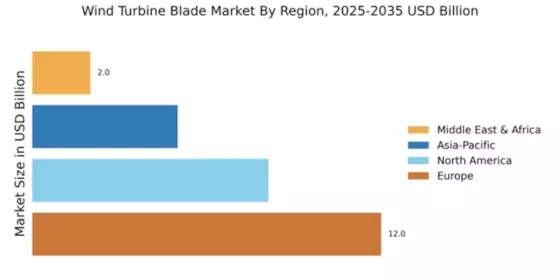
The Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry is influenced by rising concerns over energy security, as countries seek to diversify their energy sources. The geopolitical landscape and fluctuating fossil fuel prices have prompted nations to invest in renewable energy, particularly wind power. This shift is evident in regions like Europe, where countries are aggressively expanding their wind energy capacity to reduce reliance on imported fuels. The growing emphasis on energy independence is likely to drive the demand for wind turbine blades, contributing to the market's anticipated growth trajectory in the coming years.
Technological Advancements in Blade Design
Innovations in blade design and materials are pivotal for the Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry, enhancing efficiency and performance. Advanced composite materials, such as carbon fiber and epoxy resins, are increasingly utilized to produce lighter and more durable blades. These advancements not only improve energy capture but also extend the lifespan of turbine blades, thereby reducing maintenance costs. The integration of smart technologies, such as sensors and IoT, further optimizes blade performance. As a result, the market is likely to witness a significant increase in demand, aligning with the projected growth to 211.0 USD Billion by 2035.
Growing Awareness of Environmental Sustainability
There is a notable increase in public awareness regarding environmental sustainability, which significantly impacts the Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry. As consumers and businesses alike prioritize eco-friendly practices, the demand for renewable energy solutions, including wind power, continues to rise. This shift in consumer behavior is supported by educational campaigns and advocacy for cleaner energy sources. Consequently, the Global Wind Turbine Blade Market Industry is poised for growth, as more stakeholders recognize the importance of transitioning to sustainable energy systems. This trend aligns with the broader global commitment to achieving net-zero emissions.